Sonographically-guided Parasacrum Infrapiriformis Drainage of Deep Pelvic Abscesses: An Anatomical Safety Study Using SYNAPSE VINCENT
- PMID: 38689787
- PMCID: PMC11056534
- DOI: 10.23922/jarc.2023-054
Sonographically-guided Parasacrum Infrapiriformis Drainage of Deep Pelvic Abscesses: An Anatomical Safety Study Using SYNAPSE VINCENT
Abstract
Objectives: Deep pelvic abscesses are surrounded by the pelvic bones, bladder, gynecological organs, intestinal tract, and nerve and vascular systems, and are approached by various routes for drainage. The transgluteal approach is often performed under computed tomography guidance; however, if ultrasonography can be used to confirm the approach, it is considered more effective because it reduces radiation exposure and allows for real-time puncture under sonographic and fluoroscopic guidance.
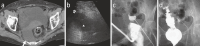
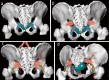
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted at Tobata Kyoritsu Hospital (Fukuoka, Japan) between April 1, 2021, and December 31, 2022. Sonographically guided transgluteal drainage with fluoroscopy was performed in five consecutive cases of deep pelvic abscesses using a 3D image analysis system (SYNAPSE VINCENT) to study the anatomy for safe puncture.
Results: Three patients had postoperative abscesses from colorectal cancer, one caused by perforation of the appendicitis, and one caused by sigmoid diverticulitis. The average drainage duration was 11 days (SD = 6.7). No complications, such as bleeding or nerve damage, were observed.
Conclusions: We constructed a 3D image of the puncture route of the trans greater sciatic foramen using SYNAPSE VINCENT to objectively comprehend the anatomy and puncture route. The ideal transgluteal approach is to insert the catheter as close to the sacrum as possible at the level of the infrapiriformis. The parasacrum infrapiriformis approach can be performed safely and easily using ultrasound guidance and fluoroscopy.
Keywords: SYNAPSE VINCENT; pelvic abscess; sonography; transgluteal drainage.
Copyright © 2024 The Japan Society of Coloproctology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transgluteal approach for percutaneous drainage of deep pelvic abscesses: 154 cases.Radiology. 2003 Sep;228(3):701-5. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2283020924. Epub 2003 Jul 24. Radiology. 2003. PMID: 12881584
-
Percutaneous trans-bladder drainage of a pelvic abscess caused by sigmoid diverticulitis: Two case reports.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Aug 9;18(10):3675-3679. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.07.059. eCollection 2023 Oct. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37601118 Free PMC article.
-
CT-guided transgluteal drainage of deep pelvic abscesses: indications, technique, procedure-related complications, and clinical outcome.Radiographics. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6):1353-67. doi: 10.1148/rg.226025039. Radiographics. 2002. PMID: 12432107 Review.
-
Transrectal sonographically guided drainage of deep pelvic abscesses.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 May;162(5):1227-30; discussion 1231-2. doi: 10.2214/ajr.162.5.8166015. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. PMID: 8166015
-
Percutaneous, computed tomography-guided drainage of deep pelvic abscesses via a transgluteal approach: a report on 30 cases and a review of the literature.Abdom Imaging. 2013 Apr;38(2):285-9. doi: 10.1007/s00261-012-9917-z. Abdom Imaging. 2013. PMID: 22684488 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

