L-Thyroxine and L-thyroxine-based antimicrobials against Streptococcus pneumoniae and other Gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 38689973
- PMCID: PMC11059415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27982
L-Thyroxine and L-thyroxine-based antimicrobials against Streptococcus pneumoniae and other Gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
Objectives: The rise of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (Sp) poses a significant global health threat, urging the quest for novel antimicrobial solutions. We have discovered that the human hormone l-thyroxine has antibacterial properties. In order to explore its drugability we perform here the characterization of a series of l-thyroxine analogues and describe the structural determinants influencing their antibacterial efficacy.
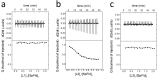
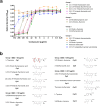
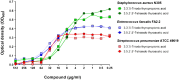
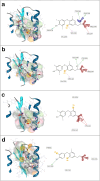
Method: We performed a high-throughput screening of a library of compounds approved for use in humans, complemented with ITC assays on purified Sp-flavodoxin, to pinpoint molecules binding to this protein. Antimicrobial in vitro susceptibility assays of the hit compound (l-thyroxine) as well as of 13 l-thyroxine analogues were done against a panel of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Toxicity of compounds on HepG2 cells was also assessed. A combined structure-activity and computational docking analysis was carried out to uncover functional groups crucial for the antimicrobial potency of these compounds.
Results: Human l-thyroxine binds to Sp-flavodoxin, forming a 1:1 complex of low micromolar Kd. While l-thyroxine specifically inhibited Sp growth, some derivatives displayed activity against other Gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis, while remaining inactive against Gram-negative pathogens. Neither l-thyroxine nor some selected derivatives exhibited toxicity to HepG2 cells.
Conclusions: l-thyroxine derivatives targeting bacterial flavodoxins represent a new and promising class of antimicrobials.
Keywords: Drug repurposing; Flavodoxin; High-throughput screening; Narrow-spectrum antibiotics; Target-oriented drug discovery.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective Targeting of Human and Animal Pathogens of the Helicobacter Genus by Flavodoxin Inhibitors: Efficacy, Synergy, Resistance and Mechanistic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 20;22(18):10137. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810137. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576300 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, molecular docking study, and antibacterial evaluation of some new fluoroquinolone analogues bearing a quinazolinone moiety.Daru. 2020 Dec;28(2):661-672. doi: 10.1007/s40199-020-00373-6. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Daru. 2020. PMID: 33030668 Free PMC article.
-
[The history of the development and changes of quinolone antibacterial agents].Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003;38(2):161-79. Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 15143768 Japanese.
-
Sulopenem: An Intravenous and Oral Penem for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):533-557. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01688-1. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35294769 Review.
-
In-vitro profile of a new beta-lactam, ceftobiprole, with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Jun;13 Suppl 2:17-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01722.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17488372 Review.
References
-
- Christensen J.S., Jensen T.G., Kolmos H.J., Pedersen C., Lassen A. Bacteremia with Streptococcus pneumoniae: sepsis and other risk factors for 30-day mortality--a hospital-based cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2012;31:2719–2725. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1619-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Djurdjevic N., Taweesedt P.T., Paulson M., LaNou A., Radovanovic M., Patel J.N., Veselinovic M., McDermott W.R., Dumic I. Septic shock and purpura fulminans due to Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia in an unvaccinated immunocompetent adult: case report and review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020;21 doi: 10.12659/AJCR.923266. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Factsheet about pneumococcal disease, (n.d.). https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/pneumococcal-disease/facts (accessed March 6, 2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

