The impact of genetic variants related to vitamin D and autoimmunity: A systematic review
- PMID: 38689997
- PMCID: PMC11059421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27700
The impact of genetic variants related to vitamin D and autoimmunity: A systematic review
Abstract
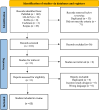
Over the past few years, there has been a notable increment in scientific literature aimed at unraveling the genetic foundations of vitamin D signaling and its implications for susceptibility to autoimmunity, however, most of them address isolated diseases. Here, we conducted a systematic review of genetic variants related to vitamin D and autoimmune diseases and we discussed the current landscape of susceptibility and outcomes. Of 65 studies analyzed, most variants cited are in vitamin D binding protein (VDBP; rs2282679 GC gene), 25-hydroxylase (rs10751657 CYP2R1), 1α-hydroxylase (rs10877012, CYP27B1) and the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily [FokI (rs2228570), BsmI (rs1544410), ApaI (rs7975232), and TaqI (rs731236) in VDR gene]. Therefore, our findings confirmed the associations of several genetic variants of vitamin D signaling with a broad spectrum of autoimmune diseases/traits. In addition, given the low number of papers found with functional analysis, further studies to elucidate the real effect that the variants exert on Vitamin D signaling are recommended.
Keywords: And outcomes; Autoimmune diseases; Genetic variants; Susceptibility; Vitamin D.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of Vitamin D Metabolism Gene Polymorphisms with Autoimmunity: Evidence in Population Genetic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9626. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249626. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship Between the ApaI (rs7975232), BsmI (rs1544410), FokI (rs2228570), and TaqI (rs731236) Variants in the Vitamin D Receptor Gene and Urolithiasis Susceptibility: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 15;11:234. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00234. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32346382 Free PMC article.
-
Association of vitamin D receptor gene TaqI, BsmI, FokI and ApaI polymorphisms and susceptibility to extremity chronic osteomyelitis in Chinese population.Injury. 2016 Aug;47(8):1655-60. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Injury. 2016. PMID: 27329975
-
Association of vitamin D receptor gene variants with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis.BMC Med Genet. 2019 Feb 14;20(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12881-019-0763-5. BMC Med Genet. 2019. PMID: 30764792 Free PMC article.
-
Association of vitamin D receptor BsmI (rs1544410), Fok1 (rs2228570), TaqI (rs731236) and ApaI (rs7975232) gene polymorphism with the nephrolithiasis susceptibility.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015 Apr;35(2):107-14. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2014.936459. Epub 2014 Jul 22. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015. PMID: 25051494
Cited by
-
Associations Between Polymorphisms of Genes Related to Vitamin D Pathway and the Response to Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 29;13(23):7277. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237277. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685734 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Mechanisms and Biomarkers Associated with T-Cells and B-Cells in Autoimmune Disorders.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Feb 11;68(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09022-9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39932617 Review.
-
Global Trends in Vitamin D Research From 1985 to 2024.PRiMER. 2025 Jun 30;9:33. doi: 10.22454/PRiMER.2025.538113. eCollection 2025. PRiMER. 2025. PMID: 40727867 Free PMC article.
-
Search for Disease-Specific Genetic Markers Originated from the Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Polymorphisms in the Multiple Sclerosis Cohort in the Latvian Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2555. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062555. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141197 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

