Burden of gallstone disease in the United States population: Prepandemic rates and trends
- PMID: 38690054
- PMCID: PMC11056655
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i4.1130
Burden of gallstone disease in the United States population: Prepandemic rates and trends
Abstract
Background: Gallstone disease is one of the most common digestive disorders in the United States and leads to significant morbidity, mortality, and health care utilization.
Aim: To expand on earlier findings and investigate prepandemic rates and trends in the gallstone disease burden in the United States using national survey and claims databases.
Methods: The National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, National Inpatient Sample, Nationwide Emergency Department Sample, Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample, Vital Statistics of the United States, Optum Clinformatics® Data Mart, and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Medicare 5% Sample and Medicaid files were used to estimate claims-based prevalence, medical care including cholecystectomy, and mortality with a primary or other gallstone diagnosis. Rates were age-adjusted (for national databases) and shown per 100000 population.
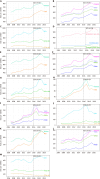
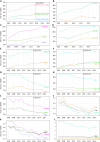
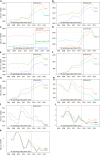
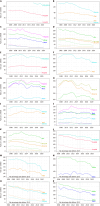
Results: Gallstone disease prevalence (claims-based, 2019) was 0.70% among commercial insurance enrollees, 1.03% among Medicaid beneficiaries, and 2.09% among Medicare beneficiaries and rose over the previous decade. Recently, in the United States population, gallstone disease contributed to approximately 2.2 million ambulatory care visits, 1.2 million emergency department visits, 625000 hospital discharges, and 2000 deaths annually. Women had higher medical care rates with a gallstone disease diagnosis, but mortality rates were higher among men. Hispanics had higher ambulatory care visit and hospital discharge rates compared with Whites, but not mortality rates. Blacks had lower ambulatory care visit and mortality rates, but similar hospital discharge rates compared with whites. During the study period, ambulatory care and emergency department visit rates with a gallstone disease diagnosis rose, while hospital discharge and mortality rates declined. Among commercial insurance enrollees, rates were higher compared with national data for ambulatory care visits and hospitalizations, but lower for emergency department visits. Cholecystectomies performed in the United States included 605000 ambulatory laparoscopic, 280000 inpatient laparoscopic, and 49000 inpatient open procedures annually. Among commercial insurance enrollees, rates were higher compared with national data for laparoscopic procedures.
Conclusion: The gallstone disease burden in the United States is substantial and increasing, particularly among women, Hispanics, and older adults with laparoscopic cholecystectomy as the mainstay treatment. Current practice patterns should be monitored for better health care access.
Keywords: Burden; Cholecystectomy; Cholelithiasis; Epidemiology; Gallstone disease; Gallstones; Health care use; Mortality.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Everhart JE, Khare M, Hill M, Maurer KR. Prevalence and ethnic differences in gallbladder disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:632–639. - PubMed
-
- Unalp-Arida A, Der JS, Ruhl CE. Longitudinal Study of Comorbidities and Clinical Outcomes in Persons with Gallstone Disease Using Electronic Health Records. J Gastrointest Surg. 2023;27:2843–2856. - PubMed
-
- Unalp-Arida A, Ruhl CE. Increasing gallstone disease prevalence and associations with gallbladder and biliary tract mortality in the US. Hepatology. 2023;77:1882–1895. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part III: Liver, biliary tract, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1134–1144. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

