Utility of expression of 4-hydroxynonenal tested by immunohistochemistry for cervical cancer
- PMID: 38690070
- PMCID: PMC11056727
- DOI: 10.5114/pm.2024.136356
Utility of expression of 4-hydroxynonenal tested by immunohistochemistry for cervical cancer
Abstract
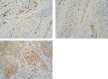
Introduction: Cervical cancer (CC) is a leading cause of mortality in women around the world, with the highest incidence rate still being in developing countries. The most common aetiological factor is infection with high-risk human papilloma virus viral strains. Oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species leads to lipid peroxidation and DNA damage. Studies show that reactive lipid electrophiles such as 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) produced in the process play an important role in cancer signalling pathways and are a good biomarker for oxidative stress. We aim to investigate the prognostic role of 4-HNE as a biomarker for oxidative stress in patients in early and advanced stages of CC measured by immunohistochemistry.
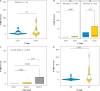
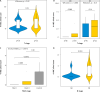
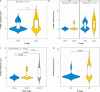
Material and methods: This is a retrospective study of 69 patients treated at our Department of Oncogynaecology. Paraffin embedded tumour tissues were immunohistochemically tested for the levels of expression of 4-HNE. The results for H-score, Allred score, and combined score were investigated for association with tumour size, lymph node status, andInternational Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics stage.
Results: 4-hydroxynonenal showed higher expression in more advanced stages of CC and in cases with involved lymph nodes. Tumour size was not associated with the levels of 4-HNE.
Conclusions: To best of our knowledge, this is the first study to use immunohistochemistry to examine the expression of 4-HNE as a prognostic factor in CC. The 3 score systems showed similar results. The pattern of 4-HNE histological appearance is dependent on the histological origin of cancer and is not universal.
Keywords: 4-HNE; ROS; cervical cancer; lipid metabolism; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of ROMO1 on cervical cancer progression.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154561. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154561. Epub 2023 May 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37285738
-
Inflammation and oxidative stress induced by lipid peroxidation metabolite 4-hydroxynonenal in human corneal epithelial cells.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Aug;258(8):1717-1725. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04647-2. Epub 2020 May 22. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32445015
-
Post-mortem Findings of Inflammatory Cells and the Association of 4-Hydroxynonenal with Systemic Vascular and Oxidative Stress in Lethal COVID-19.Cells. 2022 Jan 27;11(3):444. doi: 10.3390/cells11030444. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159254 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lipid peroxidation derived 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in cancer: focusing on mitochondria.Redox Biol. 2015;4:193-9. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25598486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer growth regulation by 4-hydroxynonenal.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Oct;111:226-234. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.030. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28131901 Review.
Cited by
-
Participation of lipids in the tumor response to photodynamic therapy and its exploitation for therapeutic gain.J Lipid Res. 2025 Feb;66(2):100729. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100729. Epub 2024 Dec 14. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 39675508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith JS, Lindsay L, Hoots B, et al. . Human papillomavirus type distribution in invasive cervical cancer and high-grade cervical lesions: a meta-analysis update. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 621-632. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
