Patient-specific quantification of cardiorespiratory motion for cardiac stereotactic radioablation treatment planning
- PMID: 38690147
- PMCID: PMC11056453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hroo.2024.03.006
Patient-specific quantification of cardiorespiratory motion for cardiac stereotactic radioablation treatment planning
Abstract
Background: Cardiac radioablation is a new treatment for patients with refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT). The target for cardiac radioablation is subject to cardiorespiratory motion (CRM), the heart's movement with breathing and cardiac contraction. Data regarding the magnitude of target CRM are limited but are highly important for treatment planning.
Objectives: The study sought to assess CRM amplitude by using ablation catheter geometrical data.
Methods: Electroanatomic mapping data of patients undergoing catheter ablation for VT at 3 academic centers were exported. The spatial position of the ablation catheter as a function of time while in contact with endocardium was analyzed and used to quantify CRM.
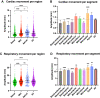
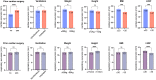
Results: Forty-four patients with ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy and VT contributed 1364 ablation lesions to the analysis. Average cardiac and respiratory excursion were 1.62 ± 1.21 mm and 12.12 ± 4.10 mm, respectively. The average ratio of respiratory to cardiac motion was approximately 11:1. CRM was greatest along the craniocaudal axis (9.66 ± 4.00 mm). Regional variations with respect to respiratory and cardiac motion were observed: basal segments had smaller displacements vs midventricular and apical segments. Patient characteristics (previous cardiac surgery, height, weight, body mass index, and left ventricular ejection fraction) had a statistically significant, albeit clinically moderate, impact on CRM.
Conclusion: CRM is primarily determined by respiratory displacement and is modulated by the location of the target and the patient's biometric characteristics. The patient-specific quantification of CRM may allow to decrease treatment volume and reduce radiation exposure of surrounding organs at risk while delivering the therapeutic dose to the target.
Keywords: 3D mapping system; Cardiac radioablation; Cardiorespiratory motion; Stereotactic body radiation therapy; Ventricular tachycardia.
© 2024 Heart Rhythm Society. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stereotactic arrhythmia radioablation for refractory scar-related ventricular tachycardia.Heart Rhythm. 2020 Aug;17(8):1241-1248. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.02.036. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Heart Rhythm. 2020. PMID: 32151737
-
Analysis of left ventricle regional myocardial motion for cardiac radioablation: Left ventricular motion analysis.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 May;25(5):e14333. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14333. Epub 2024 Mar 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38493500 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Arrhythmia Radioablation (STAR): Assessment of cardiac and respiratory heart motion in ventricular tachycardia patients - A STOPSTORM.eu consortium review.Radiother Oncol. 2023 Nov;188:109844. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109844. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Radiother Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37543057 Review.
-
A Framework for Assessing the Effect of Cardiac and Respiratory Motion for Stereotactic Arrhythmia Radioablation Using a Digital Phantom With a 17-Segment Model: A STOPSTORM.eu Consortium Study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Feb 1;118(2):533-542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.08.059. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 37652302
-
Stereotactic radioablation for ventricular tachycardia.Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2022 Mar;33(1):49-54. doi: 10.1007/s00399-021-00830-y. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 34825951 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Electrocardiogram-gated cardiac computed tomography-based patient- and segment-specific cardiac motion estimation method in stereotactic arrhythmia radioablation for ventricular tachycardia.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jan 21;33:100700. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2025.100700. eCollection 2025 Jan. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39911878 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic reconstruction and motion estimation framework for cardiorespiratory motion-resolved real-time volumetric MR imaging (DREME-MR).Phys Med Biol. 2025 Aug 8;70(17):175013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/adf9b9. Online ahead of print. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40780250 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic reconstruction and motion estimation framework for cardiorespiratory motion-resolved real-time volumetric MR imaging (DREME-MR).ArXiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 2:arXiv:2503.21014v2. ArXiv. 2025. Update in: Phys Med Biol. 2025 Aug 08. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/adf9b9. PMID: 40196152 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Al-Khatib S.M., Stevenson W.G., Ackerman M.J., et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 2018;138:e272–e391. - PubMed
-
- Neuwirth R., Cvek J., Knybel L., et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for ablation of ventricular tachycardia. Europace. 2019;21:1088–1095. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd M.S., Wight J., Schneider F., et al. Clinical experience of stereotactic body radiation for refractory ventricular tachycardia in advanced heart failure patients. Heart Rhythm. 2020;17:415–422. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

