Evaluation of salivary stress markers and inflammatory cytokine levels in peri-implantitis patients
- PMID: 38691206
- PMCID: PMC11062951
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-024-05692-5
Evaluation of salivary stress markers and inflammatory cytokine levels in peri-implantitis patients
Abstract
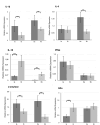
Background and objective: Psychological stress has been identified in some observational studies as a potential factor that may modify and affect periodontal diseases, but there are no similar data for peri-implantitis. The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, interferon (IFN)α inflammatory cytokines and the psychological stress-related markers, glucocorticoid receptor-α (GRα), and salivary α-amylase (sAA) gene expression levels in saliva samples obtained from healthy implants and peri-implantitis patients.
Materials and methods: The study included a total of 50 systemically healthy subjects. Peri-implant clinical parameters were recorded and psychological stress level was evaluated with the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HAD) and state-trait anxiety inventory (STAI) questionnaire forms. Following the evaluations, the patients were divided into 4 groups according their stress and clinical status (Ia, Ib, IIa, IIb). IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IFNα, GRα, sAA gene expression levels in the saliva samples were quantified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).
Results: In the group of peri-implantitis who had a high score in stress level assessment scales, significantly higher IL-1β, IL-6, sAA expression levels were observed (p < 0.001). The IL-10 gene expression levels were lower in the groups with a high score in the stress level assessment scales (p < 0.001). GRα gene was expressed at lower levels in the group of peri-implantitis who had a high score in stress level assessment scales but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.065).
Conclusion: The study findings suggest that psychological stress may increase the inflammation associated with peri-implantitis by affecting cytokine expression levels.
Clinical relevance: To prevent peri-implantitis or reduce its prevalence, it could be beneficial to evaluate stress levels and identify individuals experiencing stress.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Peri-implantitis; Psychological stress; Saliva.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of peri-implantitis: what interventions are effective? A Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012;5 Suppl:S21-41. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012. PMID: 22834392
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: treatment of peri-implantitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1(1):CD004970. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004970.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258958 Free PMC article.
-
Could cytokine levels in the peri-implant crevicular fluid be used to distinguish between healthy implants and implants with peri-implantitis? A systematic review.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Dec;51(6):689-698. doi: 10.1111/jre.12354. Epub 2016 Jan 16. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26774043
-
Levels of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), MMP-2, MMP-3, osteopontin, pentraxin-3, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in crevicular fluid samples from peri-implantitis, periodontitis, and healthy sites.J Periodontal Res. 2025 May;60(5):473-483. doi: 10.1111/jre.13338. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Periodontal Res. 2025. PMID: 39327373 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Aging-Related Secretory Phenotypic Factors in Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Peri-Implantitis: A Retrospective Analysis.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025 Aug 25;86(8):1-17. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2025.0294. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40847974
Cited by
-
Interleukin-6 Receptor Gene rs1800795 Polymorphism and Expression of Interleukin-6 in Gingival Tissue in Patients with Periodontitis.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):1954. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12101954. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458264 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation N-Telopeptide (NTx) and calprotectin level in crevicular fluid with peri-implantitis.Bioinformation. 2024 Sep 30;20(9):1183-1186. doi: 10.6026/9732063002001183. eCollection 2024. Bioinformation. 2024. PMID: 39917206 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oxytocin nasal spray pretreatment on postoperative acute stress disorder in patients with accidental traumatic fracture: a single-centre prospective randomised controlled clinical trial study protocol.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 14;15(1):e090167. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-090167. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39809565 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the association between psychological stress and peri-implant health among middle-aged and elderly adults: A systemic review.World J Clin Cases. 2025 Aug 16;13(23):105762. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.105762. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 40821403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical