pDNA-tachyplesin treatment stimulates the immune system and increases the probability of apoptosis in MC4-L2 tumor cells
- PMID: 38691208
- PMCID: PMC11062983
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-024-03393-7
pDNA-tachyplesin treatment stimulates the immune system and increases the probability of apoptosis in MC4-L2 tumor cells
Abstract
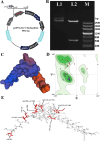
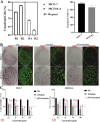
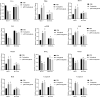
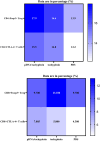
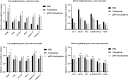
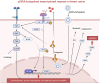
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide, and marine creatures are the most abundant reservoir of anticancer medicines. Tachyplesin peptides have shown antibacterial capabilities, but their potential to inhibit cancer growth and trigger cancer cell death has not been investigated. A synthetic tachyplesin nucleotide sequence was generated and inserted into the pcDNA3.1( +) Mammalian Expression Vector. PCR analysis and enzyme digesting procedures were used to evaluate the vectors' accuracy. The transfection efficiency of MCF-7 and MCF10-A cells was 57% and 65%, respectively. The proliferation of MCF-7 cancer cells was markedly suppressed. Administration of plasmid DNA (pDNA) combined with tachyplesin to mice with tumors did not cause any discernible morbidity or mortality throughout treatment. The final body weight curves revealed a significant reduction in weight among mice treated with pDNA/tachyplesin and tachyplesin at a dose of 100 µg/ml (18.4 ± 0.24 gr, P < 0.05; 11.4 ± 0.24 gr P < 0.01) compared to the control group treated with PBS (22 ± 0.31 gr). Animals treated with pDNA/tachyplesin and tachyplesin exhibited a higher percentage of CD4 + Foxp3 + Tregs, CD8 + Foxp3 + Tregs, and CD4 + and CD8 + T cell populations expressing CTLA-4 in their lymph nodes and spleen compared to the PBS group. The groups that received pDNA/tachyplesin exhibited a substantial upregulation in the expression levels of caspase-3, caspase-8, BAX, PI3K, STAT3, and JAK genes. The results offer new possibilities for treating cancer by targeting malignancies using pDNA/tachyplesin and activating the mTOR and NFκB signaling pathways.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immune response; Signaling pathways; Tachyplesin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dermaseptin B2 bioactive gene's potential for anticancer and anti-proliferative effect is linked to the regulation of the BAX/BBC3/AKT pathway.Med Oncol. 2024 May 20;41(6):162. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02384-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38767753
-
Tachyplesin induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells and enhances the chemosensitivity of A549/DDP cells to cisplatin by activating Fas and necroptosis pathway.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Apr;97(4):809-820. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13810. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33245189
-
Effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on proliferation and gene expression of human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line BGC-823.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 21;12(11):1694-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1694. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16586536 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of EPSTI1/Drp1/AKT1 Signaling Pathways Using pDNA/Melittin Against Breast Cancer.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jun;63(3):2276-2298. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10806-5. Epub 2024 May 9. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38722433
-
Structure-function relationships of tachyplesins and their analogues.Ciba Found Symp. 1994;186:160-74; discussion 174-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470514658.ch10. Ciba Found Symp. 1994. PMID: 7768150 Review.
References
-
- Ahmad A, Mubarak NM, Jannat FT, Ashfaq T, Santulli C, Rizwan M, Najda A, Bin-Jumah M, Abdel-Daim MM, Hussain S, Ali S (2021) A critical review on the synthesis of natural sodium alginate based composite materials: an innovative biological polymer for biomedical delivery applications. Processes 9(1):137
-
- Ahmed S, Mirzaei H, Aschner M, Khan A, Al-Harrasi A, Khan H (2021) Marine peptides in breast cancer: therapeutic and mechanistic understanding. Biomed Pharmacother 1(142):112038 - PubMed
-
- Asadipour E, Asgari M, Mousavi P, Piri-Gharaghie T, Ghajari G, Mirzaie A (2023) Nano-biotechnology and challenges of drug delivery system in cancer treatment pathway. Chem Biodivers 1:e202201072 - PubMed
-
- Balandrin MF, Klocke JA, Wurtele ES, Bollinger WH (1985) Natural plant chemicals: sources of industrial and medicinal materials. Science 228(4704):1154–1160 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

