Patient-specific beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold for customized alveolar ridge augmentation: a case report : Case Report: patient-specific β-TCP scaffold for alveolar ridge CBR
- PMID: 38691252
- PMCID: PMC11063008
- DOI: 10.1186/s40729-024-00541-2
Patient-specific beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold for customized alveolar ridge augmentation: a case report : Case Report: patient-specific β-TCP scaffold for alveolar ridge CBR
Abstract
Background: Beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) is a biocompatible ceramic material widely used in the field of oral regeneration. Due to its excellent biological and mechanical properties, it is increasingly utilized for alveolar ridge augmentation or guided bone regeneration (GBR). With recent advances in computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), β-TCP can now be used in the form of digitally designed patient-specific scaffolds for customized bone regeneration (CBR) of advanced defects in a two-stage implant therapy concept. In this case report following the CARE case report guidelines, we present a novel application of a patient-specific β-TCP scaffold in pre-implant mandibular alveolar ridge augmentation.
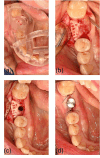
Case presentation: A 63-year-old female patient with significant horizontal bone loss in the posterior mandible was treated with a custom β-TCP scaffold in the context of a two-stage backward-planned implant therapy. Cone-beam computed tomography nine months after augmentation showed successful integration of the scaffold into the surrounding bone, allowing implant placement. Follow-up until two years after initial surgery showed excellent oral and peri-implant health.
Conclusions: This case highlights the potential of patient-specific β-TCP scaffolds for alveolar ridge augmentation and their advantage over traditional techniques, including avoidance of xeno-, allo-, and autografts. The results provide encouraging evidence for their use in clinical practice. Patient-specific β-TCP scaffolds may be a promising alternative for clinicians seeking to provide their patients with safe, predictable, and effective alveolar ridge augmentation results in customized bone regeneration procedures.
Keywords: CBR; Case report; Customized bone regeneration; Guided bone regeneration; Two-stage implant therapy; beta-tricalcium phosphate; β-TCP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Custom-made computer-aided-design/ computer-assisted-manufacturing (CAD/CAM) synthetic bone grafts for alveolar ridge augmentation: A retrospective clinical study with 3 years of follow-up.J Dent. 2022 Dec;127:104323. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2022.104323. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Dent. 2022. PMID: 36241044
-
Lateral ridge augmentation using a PCL-TCP scaffold in a clinically relevant but challenging micropig model.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Dec;23(12):1322-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02366.x. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. PMID: 22145939
-
Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (β-TCP) for Customized Bone Regeneration (CBR) in the Aesthetic Area of the Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Ridge.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025 Jun 25;0(0):1-18. doi: 10.11607/jomi.11352. Online ahead of print. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025. PMID: 40560753
-
Bone Augmentation Techniques for Horizontal and Vertical Alveolar Ridge Deficiency in Oral Implantology.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2019 May;31(2):163-191. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2019.01.005. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30947846 Review.
-
Complex bone augmentation in alveolar ridge defects.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2015 May;27(2):227-44. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2015.01.003. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 25951958 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphometric, Biomechanical and Macromolecular Performances of β-TCP Macro/Micro-Porous Lattice Scaffolds Fabricated via Lithography-Based Ceramic Manufacturing for Jawbone Engineering.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jun 28;16(7):237. doi: 10.3390/jfb16070237. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40710452 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional printed bioresorbable scaffold for maxillofacial bone reconstruction: A Scoping Review.Braz Dent J. 2024 Oct 25;35:e246112. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440202406112. eCollection 2024. Braz Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39476112 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Bone Repair with β-TCP-Based Composite Scaffolds: A Review of Design Strategies and Biological Mechanisms.Orthop Res Rev. 2025 Jul 14;17:313-340. doi: 10.2147/ORR.S525959. eCollection 2025. Orthop Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40688750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Urban I, Montero E, Sanz-Sánchez I, Palombo D, Monje A, Tommasato G, et al. Minimal invasiveness in vertical ridge augmentation. Periodontol 2000. 2023;91(1):126–44. - PubMed
-
- Boogaard MJ, Santoro F, Romanos GE. Mesh Ridge Augmentation Using CAD/ CAM Technology for Design and Printing: Two Case Reports. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2022;43(10):654–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

