Serratus Anterior Plane Blocks for Early Rib Fracture Pain Management: The SABRE Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38691350
- PMCID: PMC11063926
- DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.0969
Serratus Anterior Plane Blocks for Early Rib Fracture Pain Management: The SABRE Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Rib fractures secondary to blunt thoracic trauma typically result in severe pain that is notoriously difficult to manage. The serratus anterior plane block (SAPB) is a regional anesthesia technique that provides analgesia to most of the hemithorax; however, SAPB has limited evidence for analgesic benefits in rib fractures.
Objective: To determine whether the addition of an SAPB to protocolized care bundles increases the likelihood of early favorable analgesic outcomes and reduces opioid requirements in patients with rib fractures.
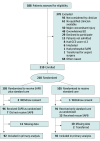
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter, open-label, pragmatic randomized clinical trial was conducted at 8 emergency departments across metropolitan and regional New South Wales, Australia, between April 12, 2021, and January 22, 2022. Patients aged 16 years or older with clinically suspected or radiologically proven rib fractures were included in the study. Participants were excluded if they were intubated, transferred for urgent surgical intervention, or had a major concomitant nonthoracic injury. Data were analyzed from September 2022 to July 2023.
Interventions: Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive an SAPB in addition to usual rib fracture management or standard care alone.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was a composite pain score measured 4 hours after enrollment. Patients met the primary outcome if they had a pain score reduction of 2 or more points and an absolute pain score of less than 4 out of 10 points.
Results: A total of 588 patients were screened, of whom 210 patients (median [IQR] age, 71 [55-84] years; 131 [62%] male) were enrolled, with 105 patients randomized to receive an SAPB plus standard care and 105 patients randomized to standard care alone. In the complete-case intention-to-treat primary outcome analysis, the composite pain score outcome was reached in 38 of 92 patients (41%) in the SAPB group and 18 of 92 patients (19.6%) in the control group (relative risk [RR], 0.73; 95% CI, 0.60-0.89; P = .001). There was a clinically significant reduction in overall opioid consumption in the SAPB group compared with the control group (eg, median [IQR] total opioid requirement at 24 hours: 45 [19-118] vs 91 [34-155] milligram morphine equivalents). Rates of pneumonia (6 patients [10%] vs 7 patients [11%]), length of stay (eg, median [IQR] hospital stay, 4.2 [2.2-7.7] vs 5 [3-7.3] days), and 30-day mortality (1 patient [1%] vs 3 patients [4%]) were similar between the SAPB and control groups.
Conclusions and relevance: This randomized clinical trial found that the addition of an SAPB to standard rib fracture care significantly increased the proportion of patients who experienced a meaningful reduction in their pain score while also reducing in-hospital opioid requirements.
Trial registration: http://anzctr.org.au Identifier: ACTRN12621000040864.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Zhen L, Bright M, McHugh M, Reardon D, White L. Serratus anterior block for rib fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Reg Anaesth. 2022;3(2):76-82. doi:10.13107/ijra.2022.v03i02.058 - DOI
-
- May L, Hillermann C, Patil S. Rib fracture management. BJA Educ. 2016;16(1):26-32. doi:10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkv011 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

