Protocol for a comprehensive pipeline to study ancient human genomes
- PMID: 38691462
- PMCID: PMC11070629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.102985
Protocol for a comprehensive pipeline to study ancient human genomes
Abstract
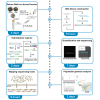
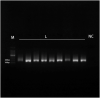
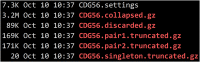
Ancient genomics has revolutionized our understanding of human evolution and migration history in recent years. Here, we present a protocol to prepare samples for ancient genomics research. We describe steps for releasing DNA from human remains, DNA library construction, hybridization capture, quantification, and sequencing. We then detail procedures for mapping sequence reads and population genetics analysis. This protocol also outlines challenges in extracting ancient DNA samples and authenticating ancient DNA to uncover the genetic history and diversity of ancient populations. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Tao et al.1.
Keywords: Genetics; Genomics; Sequence analysis; Sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
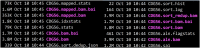



Similar articles
-
Toward high-resolution population genomics using archaeological samples.DNA Res. 2016 Aug;23(4):295-310. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsw029. Epub 2016 Jul 19. DNA Res. 2016. PMID: 27436340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for reconstructing ancestral genomes from present-day samples by applying local ancestry inference.STAR Protoc. 2025 Mar 21;6(1):103580. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.103580. Epub 2025 Jan 20. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39826116 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Capture of Ancient DNA Using Homemade Baits.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1963:93-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9176-1_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30875048
-
In-solution Y-chromosome capture-enrichment on ancient DNA libraries.BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 14;19(1):608. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4945-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30107783 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Modern Human Prehistory Using Ancient Genomes.Trends Genet. 2018 Mar;34(3):184-196. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.11.008. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 29395378 Review.
Cited by
-
Ancient genomes shed light on the genetic history of the Iron Age to historical central Xinjiang, northwest China.BMC Biol. 2025 Apr 7;23(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02195-x. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40189540 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Formation of Neolithic Hongshan People and Demic Expansion of Hongshan Culture Inferred From Ancient Human Genomes.Mol Biol Evol. 2025 Jun 4;42(6):msaf139. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaf139. Mol Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40465848 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient genomes in Southwest China revealed genetic interactions among diverse populations in the historical period.BMC Biol. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02299-4. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40597302 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient genomes from the Tang Dynasty capital reveal the genetic legacy of trans-Eurasian communication at the eastern end of Silk Road.BMC Biol. 2024 Nov 20;22(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02068-9. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39567925 Free PMC article.
-
East and West admixture in eastern China of Tang Dynasty inferred from ancient human genomes.Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 11;8(1):219. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07665-0. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39934375 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

