An HLA-E-targeted TCR bispecific molecule redirects T cell immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 38691588
- PMCID: PMC11087797
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2318003121
An HLA-E-targeted TCR bispecific molecule redirects T cell immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
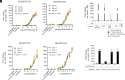
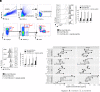
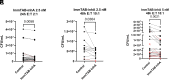
Peptides presented by HLA-E, a molecule with very limited polymorphism, represent attractive targets for T cell receptor (TCR)-based immunotherapies to circumvent the limitations imposed by the high polymorphism of classical HLA genes in the human population. Here, we describe a TCR-based bispecific molecule that potently and selectively binds HLA-E in complex with a peptide encoded by the inhA gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the causative agent of tuberculosis in humans. We reveal the biophysical and structural bases underpinning the potency and specificity of this molecule and demonstrate its ability to redirect polyclonal T cells to target HLA-E-expressing cells transduced with mycobacterial inhA as well as primary cells infected with virulent Mtb. Additionally, we demonstrate elimination of Mtb-infected cells and reduction of intracellular Mtb growth. Our study suggests an approach to enhance host T cell immunity against Mtb and provides proof of principle for an innovative TCR-based therapeutic strategy overcoming HLA polymorphism and therefore applicable to a broader patient population.
Keywords: HLA-E; T cell receptor; immunotherapy; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:R.L.P., V.A.D.S., A.W., D.G.-H., R.K., J.R.F., N.C.M., M.M., W.B., M.D., M.M.-U., T.G., C.B., D.L., C.B.-R., R.P., N. Chepisiuk, P.K.S., A.P.W., A.S.P., M.L.M., M.S., L.D., A.K., R.R., M.L., S.L., and L.F.G. are or were employees of Immunocore Ltd. A patent has been filed on the sequence and utility of the ImmTAB-inhA molecules described in this study. The authors have no additional financial interests.
Figures







Comment in
-
Weaponizing the bystander T cell army to fight tuberculosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 4;121(23):e2407559121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407559121. Epub 2024 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38814874 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Garra A., et al. , The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 31, 475–527 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Jasenosky L. D., Scriba T. J., Hanekom W. A., Goldfeld A. E., T cells and adaptive immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. Immunol. Rev. 264, 74–87 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Roberts T., Beyers N., Aguirre A., Walzl G., Immunosuppression during active tuberculosis is characterized by decreased interferon-gamma production and CD25 expression with elevated forkhead box P3, transforming growth factor-beta, and interleukin-4 mRNA levels. J. Infect. Dis. 195, 870–878 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

