A reconfigurable integrated smart device for real-time monitoring and synergistic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38691605
- PMCID: PMC11062583
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj0604
A reconfigurable integrated smart device for real-time monitoring and synergistic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
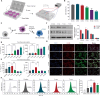
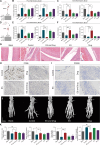
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a global autoimmune disease that requires long-term management. Ambulatory monitoring and treatment of RA favors remission and rehabilitation. Here, we developed a wearable reconfigurable integrated smart device (ISD) for real-time inflammatory monitoring and synergistic therapy of RA. The device establishes an electrical-coupling and substance delivery interfaces with the skin through template-free conductive polymer microneedles that exhibit high capacitance, low impedance, and appropriate mechanical properties. The reconfigurable electronics drive the microneedle-skin interfaces to monitor tissue impedance and on-demand drug delivery. Studies in vitro demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effect of electrical stimulation on macrophages and revealed the molecular mechanism. In a rodent model, impedance sensing was validated to hint inflammation condition and facilitate diagnosis through machine learning model. The outcome of subsequent synergistic therapy showed notable relief of symptoms, elimination of synovial inflammation, and avoidance of bone destruction.
Figures






References
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A. A., Hoy D., Smith E., Bettampadi D., Mansournia M. A., Almasi-Hashiani A., Ashrafi-Asgarabad A., Moradi-Lakeh M., Qorbani M., Collins G., Woolf A. D., March L., Cross M., Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78, 1463–1471 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Matteo A. D., Bathon J. M., Emery P., Rheumatoid arthritis. The Lancet 402, 2019–2033 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Smolen J. S., Aletaha D., Barton A., Burmester G. R., Emery P., Firestein G. S., Kavanaugh A., McInnes I. B., Solomon D. H., Strand V., Yamamoto K., Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 4, 18001 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Nikiphorou E., Santos E. J. F., Marques A., Böhm P., Bijlsma J. W., Daien C. I., Esbensen B. A., Ferreira R. J. O., Fragoulis G. E., Holmes P., McBain H., Metsios G. S., Moe R. H., Stamm T. A., de Thurah A., Zabalan C., Carmona L., Bosworth A., 2021 EULAR recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80, 1278–1285 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bodenheimer T., Patient Self-management of Chronic Disease in Primary Care. JAMA 288, 2469 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

