Highly stretchable and customizable microneedle electrode arrays for intramuscular electromyography
- PMID: 38691612
- PMCID: PMC11062587
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adn7202
Highly stretchable and customizable microneedle electrode arrays for intramuscular electromyography
Abstract
Stretchable three-dimensional (3D) penetrating microelectrode arrays have potential utility in various fields, including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. These 3D microelectrode arrays can penetrate and conform to dynamically deforming tissues, thereby facilitating targeted sensing and stimulation of interior regions in a minimally invasive manner. However, fabricating custom stretchable 3D microelectrode arrays presents material integration and patterning challenges. In this study, we present the design, fabrication, and applications of stretchable microneedle electrode arrays (SMNEAs) for sensing local intramuscular electromyography signals ex vivo. We use a unique hybrid fabrication scheme based on laser micromachining, microfabrication, and transfer printing to enable scalable fabrication of individually addressable SMNEA with high device stretchability (60 to 90%). The electrode geometries and recording regions, impedance, array layout, and length distribution are highly customizable. We demonstrate the use of SMNEAs as bioelectronic interfaces in recording intramuscular electromyography from various muscle groups in the buccal mass of Aplysia.
Figures
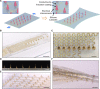
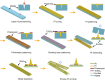
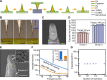
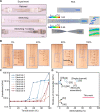

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of gold helical microwire structure electrode for long-term rodent nerve stimulation.J Neural Eng. 2025 Jun 18;22(3):036042. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ade18a. J Neural Eng. 2025. PMID: 40472863 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable Systems of Reconfigurable Microneedle Electrode Array for Subcutaneous Multiplexed Recording of Myoelectric and Electrochemical Signals.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(24):e2409075. doi: 10.1002/advs.202409075. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39679848 Free PMC article.
-
Composite additive manufacturing for suspended microelectrode arrays: Advancing oriented myocardial tissue culturing and electrophysiological sensing.Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Nov 1;287:117686. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117686. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 40523322
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the diagnostic potential of electroretinography in Parkinson's disease: A review of protocol and cohort criteria.J Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jun;15(4):694-709. doi: 10.1177/1877718X251331863. Epub 2025 Apr 29. J Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40530583 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered Microneedle System Enables the Smart Regulation of Nanodynamic Sterilization and Tissue Regeneration for Wound Management.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(9):e2412226. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412226. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39804981 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedles as transdermal drug delivery system for enhancing skin disease treatment.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Dec;14(12):5161-5180. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.08.013. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39807331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical Microneedles for Real-Time Monitoring in Interstitial Fluid: Emerging Technologies and Future Directions.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;15(6):380. doi: 10.3390/bios15060380. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexible porous microneedle array for bioelectric skin patch.Biomed Microdevices. 2025 May 10;27(2):21. doi: 10.1007/s10544-025-00749-y. Biomed Microdevices. 2025. PMID: 40347398 Free PMC article.
-
Controllable tip exposure of ultramicroelectrodes coated by diamond-like carbon via direct microplasma jet for enhanced stability and fidelity in single-cell recording.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025 Jan 23;11(1):20. doi: 10.1038/s41378-024-00819-w. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025. PMID: 39843507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren L., Liu B., Zhou W., Jiang L., A mini review of microneedle array electrode for bio-signal recording: a review. IEEE Sens. J. 20, 577–590 (2020).
-
- Ino K., Shiku H., Matsue T., Bioelectrochemical applications of microelectrode arrays in cell analysis and engineering. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 5, 146–151 (2017).
-
- Gao W., Nyein H. Y. Y., Shahpar Z., Fahad H. M., Chen K., Emaminejad S., Gao Y., Tai L.-C., Ota H., Wu E., Bullock J., Zeng Y., Lien D.-H., Javey A., Wearable microsensor array for multiplexed heavy metal monitoring of body fluids. ACS Sens. 1, 866–874 (2016).
-
- Aqrawe Z., Montgomery J., Travas-Sejdic J., Svirskis D., Conducting polymers for neuronal microelectrode array recording and stimulation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 257, 753–765 (2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

