Discontinuation of brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): a scoping review
- PMID: 38693334
- PMCID: PMC11343946
- DOI: 10.1007/s43390-024-00882-3
Discontinuation of brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): a scoping review
Abstract
Purpose: Brace treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is usually prescribed for 20-40° curves in patients with growth potential. The aim is to reduce the risk of curve progression during growth and to avoid the curve reaching a surgical threshold. Having as small a curve as possible at skeletal maturity will reduce the risk of curve progression during adult life. While evidence exists for brace treatment in AIS, there is disagreement on how and when to discontinue bracing. The purpose of this review was to investigate what criteria have been reported for initiating brace cessation and published weaning protocols and to look at estimates of the number of patients that may progress > 5 degrees after the end of growth.
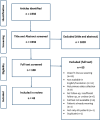
Methods: This scoping review summarizes existing knowledge on the best time to stop bracing in AIS patients, how to "wean," and what happens to spinal curves after bracing. Searches were carried out through MEDLINE, EMBASE, and PsycINFO in April 2022. A total of 1936 articles were reduced to 43 by 3 reviewers. Full papers were obtained, and data were extracted.
Results: Weaning was most commonly determined by Risser 4 (girls) and 5 (boys). Other requirements included 2 years post-menarche and no growth in standing/sitting height for 6 months. Skeletal maturity assessed from hand and wrist radiographs, e.g., Sanders' stage; distal radius and ulnar physes, could determine the optimal weaning time to minimize curve progression. Complete discontinuation was the most common option at skeletal maturity; variations on weaning protocols involved gradual reduction of bracing over 6-12 months. Curve progression after weaning is common. The 12 studies reporting early curve progression after brace weaning found a mean Cobb angle progression of 3.8° (n = 1655). From the seven studies reporting early curve progression by > 5 degrees, there were 236/700 (34%) patients. There is limited information on risk factors to predict early curve progression after finishing brace treatment with larger curves, especially those over 40 degrees possibly having more chance of progression.
Conclusion: Curve progression after bracing cessation is a negative outcome for patients who have tolerated bracing for several years, especially if surgery is required. The literature shows that when to start brace cessation and weaning protocols vary. Approximately 34% of patients progressed by more than 5 degrees at 2-4 years after brace cessation or weaning. Larger curves seem more likely to progress. More research is needed to evaluate the risk factors for curve progression after brace treatment, defining the best time to stop bracing based on the lowest risk of curve progression and whether there is any benefit to weaning.
Keywords: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; Brace discontinuation; Brace weaning; Scoping review.
© 2024. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
-
- Freidel K, Petermann F, Reichel D, Steiner A, Warschburger P, Weiss HR. Quality of life in women with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) [Internet]. 2002;27(4):E87–91. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=... - PubMed
-
- Schlenzka D, Yrjonen T. Bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Child Orthop [Internet]. 2013;7(1):51–5. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=pmnm3&NEWS=N&AN... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richards BS, Bernstein RM, D’Amato CR, Thompson GH. Standardization of criteria for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace studies: SRS Committee on Bracing and Nonoperative Management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) [Internet]. 2005;30(18):2067–8. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med6&NEWS=N&AN=... - PubMed
-
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, Dobbs MB. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2013;369(16):1512–21. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med10&NEWS=N&AN... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous