Temporal dynamics of the multi-omic response to endurance exercise training
- PMID: 38693412
- PMCID: PMC11062907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06877-w
Temporal dynamics of the multi-omic response to endurance exercise training
Abstract
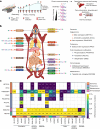
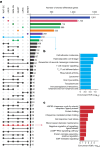
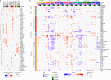
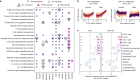
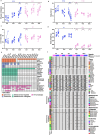
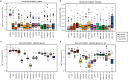
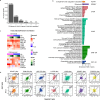
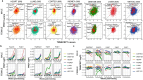
Regular exercise promotes whole-body health and prevents disease, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are incompletely understood1-3. Here, the Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium4 profiled the temporal transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, lipidome, phosphoproteome, acetylproteome, ubiquitylproteome, epigenome and immunome in whole blood, plasma and 18 solid tissues in male and female Rattus norvegicus over eight weeks of endurance exercise training. The resulting data compendium encompasses 9,466 assays across 19 tissues, 25 molecular platforms and 4 training time points. Thousands of shared and tissue-specific molecular alterations were identified, with sex differences found in multiple tissues. Temporal multi-omic and multi-tissue analyses revealed expansive biological insights into the adaptive responses to endurance training, including widespread regulation of immune, metabolic, stress response and mitochondrial pathways. Many changes were relevant to human health, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular health and tissue injury and recovery. The data and analyses presented in this study will serve as valuable resources for understanding and exploring the multi-tissue molecular effects of endurance training and are provided in a public repository ( https://motrpac-data.org/ ).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.C.B. has equity in Emmyon, Inc. G.R.C. sits on data and safety monitoring boards for AI Therapeutics, AMO Pharma, Astra-Zeneca, Avexis Pharmaceuticals, Biolinerx, Brainstorm Cell Therapeutics, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Celgene, CSL Behring, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, Green Valley Pharma, Horizon Pharmaceuticals, Immunic, Mapi Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Holdings, Opko Biologics, Prothena Biosciences, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi-Aventis, Reata Pharmaceuticals, NHLBI (protocol review committee), University of Texas Southwestern, University of Pennsylvania, Visioneering Technologies, Inc.; serves on consulting or advisory boards for Alexion, Antisense Therapeutics, Biogen, Clinical Trial Solutions LLC, Genzyme, Genentech, GW Pharmaceuticals, Immunic, Klein-Buendel Incorporated, Merck/Serono, Novartis, Osmotica Pharmaceuticals, Perception Neurosciences, Protalix Biotherapeutics, Recursion/Cerexis Pharmaceuticals, Regeneron, Roche, SAB Biotherapeutics; and is the president of Pythagoras Inc., a private consulting company. S.A.C. is a member of the scientific advisory boards of Kymera, PrognomiQ, PTM BioLabs, and Seer. M.P.S. is a cofounder and scientific advisor to Personalis, Qbio, January AI, Filtricine, SensOmics, Protos, Fodsel, Rthm, Marble and scientific advisor to Genapsys, Swaz, Jupiter. S.B.M. is a consultant for BioMarin, MyOme and Tenaya Therapeutics. D.A. is currently employed at Insitro, South San Francisco, CA. N.R.G. is currently employed at 23andMe, Sunnyvale, CA. P.M.J.B. is currently employed at Pfizer, Cambridge, MA. Insitro, 23andMe and Pfizer had no involvement in the work presented here.
Figures







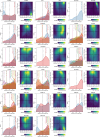
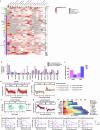
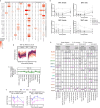


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 DK007247/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG055135/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071130/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071133/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112340/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM144269/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD026629/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112331/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG070960/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AR071113/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112348/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071158/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL154711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG055137/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG070959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD036598/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG055133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071128/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028740/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071124/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG070928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044271/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071150/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK112326/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

