Contraceptive behavior of women in India after induced abortion
- PMID: 38693522
- PMCID: PMC11064373
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-024-01802-4
Contraceptive behavior of women in India after induced abortion
Abstract
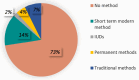
Putting an end to the silent pandemic of unsafe abortion is a major public health concern globally. Adoption of post-abortion contraception is documented as a significant contributor to reduce the number of unintended pregnancies and number of induced abortions. This study aimed at investigating the post abortion contraceptive behavior of Indian women exploring the determinants of post-abortion contraceptive uptake. Retrospective calendar data for 6,862 women aged 15-49 years from fifth round of National Family Health Survey (2019-2021) was used for the study. Multinomial logistic regression method was used to model the determinant factors to post-abortion contraceptive uptake. 72.6% women reported adopting no method of contraception after the abortion procedure. A total of 27.4% women adopted some method of contraception after abortion. 14% women preferred adopting short term modern methods. Women in early reproductive age group which is the most vulnerable group in experiencing unintended pregnancies are less likely to adopt any contraceptive method after abortion. Uptake of post abortion contraception is quite low in India. Effort should be taken in the direction of bringing awareness through provision of targeted contraceptive counselling after abortion.
Keywords: Abortion; Counselling; India; Post-abortion contraception.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cobb L, Putney P, Rochat R, Solo J, Buono N, Dunlop J, Vandenbroucke M. Global evaluation of USAID’s postabortion care program. Washington, DC: USAID; 2001.
-
- Rasch V, Huber D, Akande EO. Report of the postabortion care technical advisory panel. 2007.
-
- Babu NP, Verma RK. Abortion in India: what does the National Family Health Survey tell us? J Fam Welf. 1998;44:45–54.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical