Advances in the application of extracellular vesicles derived from three-dimensional culture of stem cells
- PMID: 38693585
- PMCID: PMC11064407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02455-y
Advances in the application of extracellular vesicles derived from three-dimensional culture of stem cells
Abstract
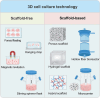
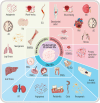
Stem cells (SCs) have been used therapeutically for decades, yet their applications are limited by factors such as the risk of immune rejection and potential tumorigenicity. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), a key paracrine component of stem cell potency, overcome the drawbacks of stem cell applications as a cell-free therapeutic agent and play an important role in treating various diseases. However, EVs derived from two-dimensional (2D) planar culture of SCs have low yield and face challenges in large-scale production, which hinders the clinical translation of EVs. Three-dimensional (3D) culture, given its ability to more realistically simulate the in vivo environment, can not only expand SCs in large quantities, but also improve the yield and activity of EVs, changing the content of EVs and improving their therapeutic effects. In this review, we briefly describe the advantages of EVs and EV-related clinical applications, provide an overview of 3D cell culture, and finally focus on specific applications and future perspectives of EVs derived from 3D culture of different SCs.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; Clinical applications; Extracellular vesicles; Stem cells; Therapeutics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
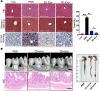
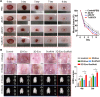
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82303775/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82172102/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BE2021689/the Jiangsu Province's Major Project in Research and Development
- Grant ss2018003/Zhenjiang Key Laboratory of High Technology Research on Exosomes Foundation and Transformation Application
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

