Comparing Neuromuscular Blockade Measurement Between Upper Arm (TOF Cuff®) and Eyelid (TOF Scan®) Using Mivacurium during General Anesthesia
- PMID: 38693676
- PMCID: PMC11075572
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943630
Comparing Neuromuscular Blockade Measurement Between Upper Arm (TOF Cuff®) and Eyelid (TOF Scan®) Using Mivacurium during General Anesthesia
Abstract
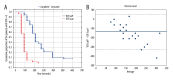
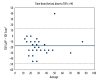
BACKGROUND Mivacurium is a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. TOF-Cuff® is a device that monitors intraoperative neuromuscular blockade and blood pressure. TOF-Scan® measures muscle relaxation status of an anaesthetized patient. This study included 36 patients aged 18 to 75 years presenting for elective surgery, to compare neuromuscular blockade measured using the TOF-Cuff of the upper arm and the TOF-Scan of the facial corrugator supercilii muscle during general anesthesia and following administration of mivacurium. MATERIAL AND METHODS Train-of-four (TOF) values were obtained every 30 s before intubation and successively every 5 min until extubation. RESULTS The median onset time for TOF-Cuff was longer than for TOF-Scan (210 s vs 90 s, P<0.00001). Multiplying the time to relaxation (according to TOF-Scan) by 1 to 8, respectively, provided concordance with the TOF-Cuff result for the following cumulative percentages of patients: 5.5%, 38.9%, 58.3%, 77.8%, 83.3%, 86.1%, 88.9%, and 91.7%. Analogue values for time to recovery from the last dose were 11.1%, 63.9%, 83.3%, 86.1%, 86.1%, 88.9%, 88.9%, and 91.7%. The proportion of patients who still had TOFratio=0 in the assessment performed at min 15 did not differ significantly between these 2 methods (P=0.088). Both TOF-Scan and TOF-Cuff showed a false-negative result in patients with clinical symptoms of preterm recovery; the numerical difference favored TOF-Cuff (1.6% vs 2.1%) but without statistical significance (P=0.2235). CONCLUSIONS When measurement on the limb is not possible, TOF-Scan on the eyelid can be an alternative for TOF-Cuff on the upper arm, if the time to relaxation is multiplied by at least 8, which is enough for 90% of patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Murphy GS, Szokol JW, Avram MJ, et al. Comparison of the TOFscan and the TOF-Watch SX during recovery of neuromuscular function. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(5):880–88. - PubMed
-
- Naguib M, Brull SJ, Kopman AF, et al. Consensus statement on perioperative use of neuromuscular monitoring. Anesth Analg. 2018;127(1):71–80. - PubMed
-
- Hemmerling TM, Schmidt J, Hanusa C, et al. Simultaneous determination of neuromuscular block at the larynx, diaphragm, adductor pollicis, orbicularis oculi and corrugator supercilii muscles. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85(6):856–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

