Saudi National Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Adult Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 38693734
- PMCID: PMC12079323
- DOI: 10.2174/0115733971275638240429063041
Saudi National Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Adult Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: To provide evidence-based clinical practice recommendations for managing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in Saudi Arabia.
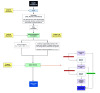
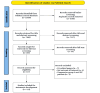
Methods: This EULAR-adapted national guideline in which a multidisciplinary task force utilized the modified Delphi method to develop 31 clinical key questions. A systematic literature review was conducted to update the evidence since the EULAR publication. After reaching a consensus agreement, two rounds of voting and group discussion were conducted to generate consolidated recommendations/ statements.
Results: A significant number of patients in Saudi Arabia experience delays in accessing rheumatologists, highlighting the significance of timely referral to SLE specialists or rheumatologists to ensure accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment. The primary goal of Glucocorticoid (GC) therapy in SLE patients is to establish disease control with a minimum dose and duration. Steroid-sparing agent utilization facilitates steroid-sparing goals. Hydroxychloroquine is recommended for all SLE patients, though physicians must carefully monitor toxicity and prioritize regular medication adherence assessment. SLE management during pregnancy starts from preconception time by assessing disease activity, major organ involvement, hypercoagulability status, and concomitant diseases that may negatively impact maternal and fetal outcomes. Multidisciplinary care with close monitoring may optimize both maternal and fetal outcomes. For patients with antiphospholipid antibodies, low-dose aspirin prophylaxis is recommended. Also, Long-term anticoagulant medications are fundamental to prevent secondary antiphospholipid syndrome due to high thrombosis recurrence.
Conclusion: This Saudi National Clinical Practice guidelines for SLE management provide evidence- based recommendations and guidance for healthcare providers in Saudi Arabia who are managing patients with SLE. These guidelines will help to standardize healthcare service, improve provider education, and perhaps lead to better treatment outcomes for SLE patients.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; Steroid-sparing agent; Systemic lupus erythematosus; disease activity; glucocorticoid.; guidelines.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors whose names are listed above certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria, educational grants, participation in speakers’ bureaus, membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #64: Systemic lupus erythematosus in pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Mar;228(3):B41-B60. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36084704
-
EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a Task Force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Feb;67(2):195-205. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.070367. Epub 2007 May 15. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 17504841
-
EULAR recommendations for women's health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Mar;76(3):476-485. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209770. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27457513 Free PMC article.
-
EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 Jun;81(6):768-779. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221733. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 35110331
-
EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jan 2;83(1):15-29. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224762. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 37827694
Cited by
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Intravenous Belimumab on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Saudi Arabia: The OBSErve Observational Study.Open Access Rheumatol. 2025 Feb 14;17:33-45. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S497802. eCollection 2025. Open Access Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39973976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boumpas D.T., Austin H.A., III, Fessler B.J., Balow J.E., Klippel J.H., Lockshin M.D. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Emerging concepts. Part 1: Renal, neuropsychiatric, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and hematologic disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995;122(12):940–950. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-12-199506150-00009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Arfaj A.S., Al-Balla S.R., Al-Dalaan A.N., Al-Saleh S.S., Bahabri S.A., Mousa M.M., Sekeit M.A. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in central Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2002;23(1):87–89. - PubMed
-
- Hassen L.M., Albarrak R.A., Albahlal R.A., Alsaqabi D.K., Hassen I.M., Daghestani M.H., Alqurtas E.M., Alkhalaf A.T., Bedaiwi M.K., Omair M.A., Almaghlouth I.A. Functional and psychosocial impact of COVID-19 pandemic on rheumatic patients’ quality of life in Saudi Arabia. Qual. Life Res. 2022;31(11):3229–3239. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03184-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous