SNS citizenship behavior based on D&M information system success model and social capital theory: Mediating role of subjective well-being
- PMID: 38694120
- PMCID: PMC11061670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29982
SNS citizenship behavior based on D&M information system success model and social capital theory: Mediating role of subjective well-being
Abstract
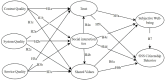
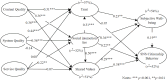
Social media has become integral to contemporary society, with online behaviors impacting individual experiences and the wider community. In Bangladesh, a developing country, SNS have played a pivotal role in the nation's digitalization efforts. This study explores the relationship between social capital theory, D&M Information System Model, subjective well-being, and SNS Citizenship Behavior (SCB) among active social media users in Bangladesh. Data was collected from 418 participants through an online survey, and hypotheses were tested using structural equation modeling. The findings indicate that the items of the D&M model positively influenced the aspects of social capital theory, excluding service quality. In contrast, social interaction ties and shared values were positively associated with SCB, although social trust did not exhibit a significant relationship. Additionally, subjective well-being mediated the connection between social capital and SCB. This research offers valuable insights into the factors influencing online prosocial behavior and provides practical implications for cultivating a positive communication culture in the digital era. The model proposed in this study holds significant implications for Bangladesh's policymakers and social networking site authorities, guiding their efforts in implementing technology-based initiatives.
Keywords: D&M system model; SNS citizenship behavior; Social capital theory; Subjective well-being.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connection and happiness: an interactive study of social media, social capital, and the subjective well-being of international students.Front Psychol. 2025 May 9;16:1548663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1548663. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40417013 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Social Network Service Use Motives and Subjective Well-Being: The Mediating Effect of Online and Offline Social Capital.Psychiatry Investig. 2023 Jun;20(6):493-503. doi: 10.30773/pi.2022.0008. Epub 2023 May 30. Psychiatry Investig. 2023. PMID: 37248692 Free PMC article.
-
Do online social interactions cultivate social capital? Evidence from a longitudinal study.Front Psychol. 2022 Oct 14;13:989137. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.989137. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36312069 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effects of social capital on the compulsive use of online social networks in civil unrest contexts.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 16;8(7):e09990. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09990. eCollection 2022 Jul. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35874073 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of social media on tourist behavior in rural mountain tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic: The role of perceived risk and community participation.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024 Feb;242:104113. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2023.104113. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38171191 Review.
Cited by
-
Connection and happiness: an interactive study of social media, social capital, and the subjective well-being of international students.Front Psychol. 2025 May 9;16:1548663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1548663. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40417013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lankton N.K., Wilson E.V., Mao E. Antecedents and determinants of information technology habit. Inf. Manag. 2010;47(5–6):300–307.
-
- Hew K.F. Students' and teachers' use of Facebook. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011;27(2):662–676.
-
- Pang H. Connecting mobile social media with psychosocial well-being: understanding relationship between WeChat involvement, network characteristics, online capital and life satisfaction. Soc. Network. 2022;68:256–263.
-
- Hossain M.M., Islam K.Z., Al Masud A., Biswas S., Hossain M.A. Behavioral intention and continued adoption of Facebook: an exploratory study of graduate students in Bangladesh during the Covid-19 pandemic. Management. 2021;25(2):153–186.
-
- Hoadley C.M., Xu H., Lee J.J., Rosson M.B. Privacy as information access and illusory control: the case of the Facebook News Feed privacy outcry. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2010;9(1):50–60.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources