Role of nutraceutical against exposure to pesticide residues: power of bioactive compounds
- PMID: 38694227
- PMCID: PMC11061536
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1342881
Role of nutraceutical against exposure to pesticide residues: power of bioactive compounds
Abstract
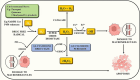
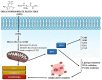
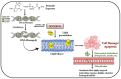
Pesticides play a crucial role in modern agriculture, aiding in the protection of crops from pests and diseases. However, their indiscriminate use has raised concerns about their potential adverse effects on human health and the environment. Pesticide residues in food and water supplies are a serious health hazards to the general public since long-term exposure can cause cancer, endocrine disruption, and neurotoxicity, among other health problems. In response to these concerns, researchers and health professionals have been exploring alternative approaches to mitigate the toxic effects of pesticide residues. Bioactive substances called nutraceuticals that come from whole foods including fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices have drawn interest because of their ability to mitigate the negative effects of pesticide residues. These substances, which include minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and polyphenols, have a variety of biological actions that may assist in the body's detoxification and healing of harm from pesticide exposure. In this context, this review aims to explore the potential of nutraceutical interventions as a promising strategy to mitigate the toxic effects of pesticide residues.
Keywords: apoptosis; cytotoxicity; nutraceuticals; pesticides; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2024 Sajad, Shabir, Singh, Bhardwaj, Alsanie, Alamri, Alhomrani, Alsharif, Vamanu and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pesticide exposure, safety issues, and risk assessment indicators.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2011 May;8(5):1402-19. doi: 10.3390/ijerph8051402. Epub 2011 May 6. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21655127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health perspective of pesticide exposure and dietary management.Malays J Nutr. 2004 Mar;10(1):39-51. Epub 2004 Mar 15. Malays J Nutr. 2004. PMID: 22691747
-
Swedish pesticide risk reduction 1981-1995: food residues, health hazard, and reported poisonings.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1996;147:119-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-4058-7_4. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1996. PMID: 8776987 Review.
-
Pesticide exposure--Egyptian scene.Toxicology. 2004 May 20;198(1-3):91-115. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2004.01.036. Toxicology. 2004. PMID: 15138034 Review.
-
Impact of pesticide polarity and lipid phase dimensions on the bioaccessibility of pesticides in agricultural produce consumed with model fatty foods.Food Funct. 2020 Jul 22;11(7):6028-6037. doi: 10.1039/c9fo03055g. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32697245
Cited by
-
Examining the Correlation between the Inorganic Nano-Fertilizer Physical Properties and Their Impact on Crop Performance and Nutrient Uptake Efficiency.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jul 28;14(15):1263. doi: 10.3390/nano14151263. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39120369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Sex-Related Effects of Dietary Polyphenols and Metabolic Disruptors on Inflammatory and (Neuro) Endocrine Pathways in Obesity: The HEAL Project.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 23;16(21):3595. doi: 10.3390/nu16213595. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519428 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and antioxidant effects of Urtica dioica extract against chlorpyrifos-induced toxicity: an in vivo study.3 Biotech. 2025 Apr;15(4):86. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04239-z. Epub 2025 Mar 12. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40092451
-
Integrated Biomarker Response Emphasizing Neuronal Oxidative Stress and Genotoxicity Induced by Oxamyl in Sprague Dawley Rats: Ameliorative Effect of Ginseng as a Neuroprotective Agent.Toxics. 2024 Sep 7;12(9):655. doi: 10.3390/toxics12090655. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39330583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaur N, Diwan B, Choudhary R. Bioremediation of organic pesticides using nanomaterials. nano-bioremediation: Fundamentals and Applications. Micro Nano Technol. (2022) 2022:517–40. 10.1016/B978-0-12-823962-9.00024-6 - DOI
-
- Van Boxstael S, Habib I, Jacxsens L, De Vocht M, Baert L, Van de Perre E, et al. Food safety issues in fresh produce: Bacterial pathogens, viruses and pesticide residues indicated as major concerns by stakeholders in the fresh produce chain. Food Control. (2013) 32:190–7. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.11.038 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

