Persistence to Basal Insulin: Association With Health Outcomes in a Population With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 38694243
- PMCID: PMC11060632
- DOI: 10.2337/cd23-0016
Persistence to Basal Insulin: Association With Health Outcomes in a Population With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
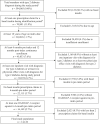
This study examined the association between persistence to basal insulin and clinical and economic health outcomes. The question of whether a persistence measure for basal insulin could be leveraged in quality measurement was also explored. Using the IBM-Truven MarketScan Commercial and Medicare Supplemental Databases from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2015, a total of 14,126 subjects were included in the analyses, wherein 9,898 (70.1%) were categorized as persistent with basal insulin therapy. Basal insulin persistence was associated with lower A1C, fewer hospitalizations and emergency department visits, and lower health care expenditures. Quality measures based on prescription drug claims for basal insulin are feasible and should be considered for guiding quality improvement efforts.
©2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States. Available from https://www.cdc. gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html. Accessed 16 June 2022
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Diabetes Translation . Long-term trends in diabetes. Available from https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/42550/cdc_ 42550_DS1.pdf. Accessed 1 November 2022
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

