ST2 levels and neurodegenerative diseases: is this a significant relation?
- PMID: 38694387
- PMCID: PMC11060292
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001939
ST2 levels and neurodegenerative diseases: is this a significant relation?
Abstract
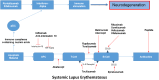
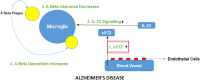
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), belonging to the interleukin-1 cytokine family, has a decoy receptor soluble ST2 (sST2). IL-33 is found in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes and is involved in central nervous system healing and repair, whereas ST2 is found in microglia and astrocytes. Some studies have found a link between changes in the IL-33/ST2 pathway and neurodegenerative disorders. This review article investigates the relationship between the interleukin-33 (IL-33)/ST2 pathway and neurodegenerative disorders. It was discovered that soluble st2 levels were increased. Furthermore, IL-33 levels were found to be lower in many neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The association with other disorders, such as ankylosing spondylitis, multiple sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), was also observed. Various studies suggest that ST2/IL-33 signalling may be pivotal in the disease modulation of neurodegenerative disorders. The serum sST2 level test can be useful in determining the inflammatory status and severity of illness in many neurodegenerative disorders. In this review, we will discuss recent findings concerning the interleukin-33 (IL-33)/ST2 pathway and its role in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases with neurodegeneration.
Keywords: IL-33; central nervous system (CNS); neurodegenerative disorders; soluble ST2 levels.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Trajkovic V, Sweet MJ, Xu D. T1/ST2 - An IL-1 receptor-like modulator of immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2004;15(2–3):87–95. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. An IL-1 family member requires caspase-1 processing and signals through the ST2 receptor. Immunity 2005;23:461–2. - PubMed
-
- Liew FY, Pitman NI, McInnes IB. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: the new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat Rev Immunol 2010;10:103–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous