High interleukin-6 levels induced by COVID-19 pneumonia correlate with increased circulating follicular helper T cell frequency and strong neutralization antibody response in the acute phase of Omicron breakthrough infection
- PMID: 38694512
- PMCID: PMC11061453
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1377014
High interleukin-6 levels induced by COVID-19 pneumonia correlate with increased circulating follicular helper T cell frequency and strong neutralization antibody response in the acute phase of Omicron breakthrough infection
Abstract
Background: Acute immune responses to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are influenced by variants, vaccination, and clinical severity. Thus, the outcome of these responses may differ between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients and those with and without COVID-19-related pneumonia. In this study, these differences during infection with the Omicron variant were investigated.
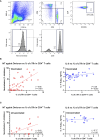
Methods: A total of 67 patients (including 47 vaccinated and 20 unvaccinated patients) who were hospitalized within 5 days after COVID-19 symptom onset were enrolled in this prospective observational study. Serum neutralizing activity was evaluated using a pseudotyped virus assay and serum cytokines and chemokines were measured. Circulating follicular helper T cell (cTfh) frequencies were evaluated using flow cytometry.
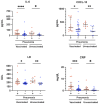
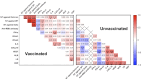
Results: Twenty-five patients developed COVID-19 pneumonia on hospitalization. Although the neutralizing activities against wild-type and Delta variants were higher in the vaccinated group, those against the Omicron variant as well as the frequency of developing pneumonia were comparable between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. IL-6 and CXCL10 levels were higher in patients with pneumonia than in those without it, regardless of their vaccination status. Neutralizing activity against the Omicron variant were higher in vaccinated patients with pneumonia than in those without it. Moreover, a distinctive correlation between neutralizing activity against Omicron, IL-6 levels, and cTfh proportions was observed only in vaccinated patients.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates the existence of a characteristic relationship between neutralizing activity against Omicron, IL-6 levels, and cTfh proportions in Omicron breakthrough infection.
Keywords: Omicron; circulating follicular helper T cell; interleukin-6; neutralizing antibody; pneumonia.
Copyright © 2024 Kawasuji, Morinaga, Nagaoka, Tani, Yoshida, Yamada, Takegoshi, Kaneda, Murai, Kimoto, Niimi and Yamamoto.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Menni C, Valdes AM, Polidori L, Antonelli M, Penamakuri S, Nogal A, et al. . Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study. Lancet (London England). (2022) 399:1618–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00327-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

