Diagnostic value of exosomal noncoding RNA in lung cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 38694786
- PMCID: PMC11061461
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1357248
Diagnostic value of exosomal noncoding RNA in lung cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is one of the most dangerous cancers in the world. Most lung cancer patients are diagnosed in the middle and later stages, which can lead to poor survival rates. The development of lung cancer is often accompanied by abnormal expression of exosomal non-coding RNAs, which means that they have the potential to serve as noninvasive novel molecular markers for lung cancer diagnosis.
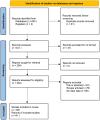
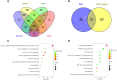
Methods: For this study, we conducted a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, Web of science, Science direct, Embase, Cochrane, and Medline databases, and by reviewing published literature, The diagnostic capacity of exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs), long-chain non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) for lung cancer was evaluated. Functional enrichment analysis of miRNA target genes was performed.
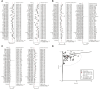
Results: The study included 41 papers, a total of 68 studies. More than 60 miRNAs, 9 lncRNAs and 14 circRNAs were involved. The combined sensitivity and specificity were 0.83(95%CI, 0.80~0.86) and 0.83(95% CI,0.79~0.87); 0.71(95% CI,0.68~0.74) and 0.79(95%CI, 0.75~0.82); 0.79(95%CI,0.67~0.87) and 0.81(95%CI,0.74~0.86), and constructed overall subject operating characteristic curves with the summarized area under the curve values of 0.90, 0.82, and 0.86.
Conclusion: Our study shows that exosomes miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs are effective in the diagnosis of lung cancer, providing evidence for studies related to novel lung cancer diagnostic markers.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023457087.
Keywords: circRNA; exosome; lncRNA; lung cancer; miRNA.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Liu, Liu, Su, Liu, Yang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1362437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38524131 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on the Biomarker Potential of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer: An In Silico Characterization of Related Exosomal lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-Target Axis.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1081. doi: 10.3390/cells12071081. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of circulating exosomal circRNAs in malignances: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 May 26;102(21):e33872. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033872. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37233410 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA profiles of umbilical cord blood exosomes from preterm newborns showing bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Sep;181(9):3345-3365. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04544-2. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35790551 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and diagnostic value of circRNA expression in cervical cancer: a meta analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 13;14:1488040. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1488040. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39871946 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in human malignancies: biological functions and clinical applications.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 24;42(8):279. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02845-8. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40553231 Review.
-
Expression characteristics and biological significance of exosome-related genes in lung cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 18;16(1):1373. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03173-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40681737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi JF, Wang L, Wu N, Li JL, Hui ZG, Liu SM, et al. . Clinical characteristics and medical service utilization of lung cancer in China, 2005-2014: Overall design and results from a multicenter retrospective epidemiologic survey. Lung Cancer. (2019) 128:91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.11.031 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

