Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors of twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway and their effect on the control of Campylobacter jejuni in chickens
- PMID: 38694802
- PMCID: PMC11061419
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1342573
Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors of twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway and their effect on the control of Campylobacter jejuni in chickens
Abstract
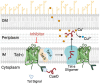
Introduction: Control of Campylobacter from farm to fork is challenging due to the frequent emergence of antimicrobial-resistant isolates. Furthermore, poultry production systems are known reservoirs of Campylobacter. The twin-arginine translocation (Tat) pathway is a crucial bacterial secretion system that allows Campylobacter to colonize the host intestinal tract by using formate as the main source of energy. However, Tat pathway is also a major contributing factor for resistance to copper sulfate (CuSO4).
Methods: Since mammals and chickens do not have proteins or receptors that are homologous to bacterial Tat proteins, identification of small molecule (SM) inhibitors targeting the Tat system would allow the development of safe and effective control methods to mitigate Campylobacter in infected or colonized hosts in both pre-harvest and post-harvest. In this study, we screened 11 commercial libraries (n = 50,917 SM) for increased susceptibility to CuSO4 (1 mM) in C. jejuni 81-176, a human isolate which is widely studied.
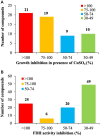
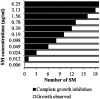
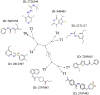
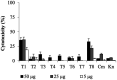
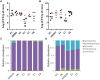
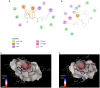
Results: Furthermore, we evaluated 177 SM hits (2.5 μg/mL and above) that increased the susceptibility to CuSO4 for the inhibition of formate dehydrogenase (Fdh) activity, a Tat-dependent substrate. Eight Tat-dependent inhibitors (T1-T8) were selected for further studies. These selected eight Tat inhibitors cleared all tested Campylobacter strains (n = 12) at >10 ng/mL in the presence of 0.5 mM CuSO4in vitro. These selected SMs were non-toxic to colon epithelial (Caco-2) cells when treated with 50 μg/mL for 24 h and completely cleared intracellular C. jejuni cells when treated with 0.63 μg/mL of SM for 24 h in the presence of 0.5 mM of CuSO4. Furthermore, 3 and 5-week-old chicks treated with SM candidates for 5 days had significantly decreased cecal colonization (up to 1.2 log; p < 0.01) with minimal disruption of microbiota. In silico analyses predicted that T7 has better drug-like properties than T2 inhibitor and might target a key amino acid residue (glutamine 165), which is located in the hydrophobic core of TatC protein.
Discussion: Thus, we have identified novel SM inhibitors of the Tat pathway, which represent a potential strategy to control C. jejuni spread on farms.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; microbiome; poultry production system; small molecule inhibitor; twin arginine translocase.
Copyright © 2024 Deblais, Drozd, Kumar, Antwi, Fuchs, Khupse, Helmy and Rajashekara.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abouelhassan Y., Garrison A. T., Burch G. M., Wong W., Norwood V. M., Huigens R. W. (2014). Discovery of quinoline small molecules with potent dispersal activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms using a scaffold hopping strategy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 24, 5076–5080. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.09.009, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agyare C., Boamah V. E., Zumbi C. N., Osei F. B. (2018). “Antibiotic use in poultry production and its effects on bacterial resistance” in Antimicrobial resistance–a global threat. ed. Kumar Y. (London: IntechOpen; )
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

