Comprehensive overview of different medicinal parts from Morus alba L.: chemical compositions and pharmacological activities
- PMID: 38694910
- PMCID: PMC11061381
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1364948
Comprehensive overview of different medicinal parts from Morus alba L.: chemical compositions and pharmacological activities
Abstract
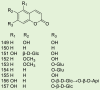
Morus alba L., a common traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with a centuries-old medicinal history, owned various medicinal parts like Mori folium, Mori ramulus, Mori cortex and Mori fructus. Different medical parts exhibit distinct modern pharmacological effects. Mori folium exhibited analgesic, anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic action and lipid-regulation effects. Mori ramulus owned anti-bacterial, anti-asthmatic and diuretic activities. Mori cortex showed counteraction action of pain, inflammatory, bacterial, and platelet aggregation. Mori fructus could decompose fat, lower blood lipids and prevent vascular sclerosis. The main chemical components in Morus alba L. covered flavonoids, phenolic compounds, alkaloids, and amino acids. This article comprehensively analyzed the recent literature related to chemical components and pharmacological actions of M. alba L., summarizing 198 of ingredients and described the modern activities of different extracts and the bioactive constituents in the four parts from M. alba L. These results fully demonstrated the medicinal value of M. alba L., provided valuable references for further comprehensive development, and layed the foundation for the utilization of M. alba L.
Keywords: Mori cortex; Mori folium; Mori fructus; Mori ramulus; chemical constituents; pharmacological activities.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Ai, Gu, Guan, Yang, Zhang, Mao, Lin, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Morus alba].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 May;47(9):2373-2391. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211123.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35531685 Chinese.
-
Comparative study of chemical composition and active components against α-glucosidase of various medicinal parts of Morus alba L.Biomed Chromatogr. 2018 Nov;32(11):e4328. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4328. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Biomed Chromatogr. 2018. PMID: 29975423
-
Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts.Molecules. 2024 Aug 23;29(17):3981. doi: 10.3390/molecules29173981. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274829 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, bioactivities and future prospective of polysaccharides from Morus alba (white mulberry): A review.Food Chem. 2018 Apr 15;245:899-910. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.11.084. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29287458 Review.
-
Can highly cited herbs in ancient Traditional Chinese medicine formulas and modern publications predict therapeutic targets for diabetes mellitus?J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;213:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.032. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29102765 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Application of a Senolytic Predictor for Discovery of Novel Senolytic Compounds and Herbs.Molecules. 2025 Jun 19;30(12):2653. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122653. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572616 Free PMC article.
-
Morus alba L. Cell Cultures as Sources of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Stilbenoids for Food Supplement Development.Molecules. 2025 May 7;30(9):2073. doi: 10.3390/molecules30092073. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363879 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry (Morus alba) Twig and Leaf Extracts Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders via Gut Microbiota Modulation in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 15;15(12):1768. doi: 10.3390/ani15121768. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564320 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Activities and Usefulness of Deoxynojirimycin and Morus alba: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2025 Jul 31;30(15):3213. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153213. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agus H. H., Cetin A., Ozdemir N., Ozbay M. G., Caglar M. A., Sariyildiz M. A., et al. (2022). Resorcinol alleviates alpha-terpineol-induced cell death in Schizosaccharomyces pombe via increased activity of the antioxidant enzyme Sod2. FEMS Yeast Res. 22 (1), foac052. 10.1093/femsyr/foac052 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous