Current and further outlook on the protective potential of Antrodia camphorata against neurological disorders
- PMID: 38694913
- PMCID: PMC11061445
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1372110
Current and further outlook on the protective potential of Antrodia camphorata against neurological disorders
Abstract
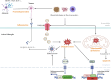
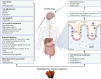
Prevalent neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke are increasingly becoming a global burden as society ages. It is well-known that degeneration and loss of neurons are the fundamental underlying processes, but there are still no effective therapies for these neurological diseases. In recent years, plenty of studies have focused on the pharmacology and feasibility of natural products as new strategies for the development of drugs that target neurological disorders. Antrodia camphorata has become one of the most promising candidates, and the crude extracts and some active metabolites of it have been reported to play various pharmacological activities to alleviate neurological symptoms at cellular and molecular levels. This review highlights the current evidence of Antrodia camphorata against neurological disorders, including safety evaluation, metabolism, blood-brain barrier penetration, neuroprotective activities, and the potential on regulating the gut-microbiome-brain axis. Furthermore, potential strategies to resolve problematic issues identified in previous studies are also discussed. We aim to provide an overview for the ongoing development and utilization of Antrodia camphorata in cerebral neuropathology.
Keywords: Antrodia camphorata; CNS disease; gut-microbiome-brain axis; neuroprotective activities; secondary metabolite.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Wan, Qiao, Liu, Peng, Zhang, Shu, Xia and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A review on the protective effect of active components in Antrodia camphorata against alcoholic liver injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;300:115740. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115740. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36162549 Review.
-
Increasing anti-Aβ-induced neurotoxicity ability of Antrodia camphorata-fermented product with deep ocean water supplementary.J Sci Food Agric. 2016 Nov;96(14):4690-4701. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7687. Epub 2016 Apr 26. J Sci Food Agric. 2016. PMID: 26919329
-
A network pharmacology-based strategy to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Antrodia camphorata and antcin K for treating type II diabetes mellitus.Phytomedicine. 2022 Feb;96:153851. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153851. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 34823968
-
Solid-state-cultured mycelium of Antrodia camphorata exerts potential neuroprotective activities against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced toxicity in PC12 cells.J Food Biochem. 2022 Aug;46(8):e14208. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14208. Epub 2022 Apr 25. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35467031
-
Review of biological and pharmacological activities of the endemic Taiwanese bitter medicinal mushroom, Antrodia camphorata (M. Zang et C. H. Su) Sh. H. Wu et al. (higher Basidiomycetes).Int J Med Mushrooms. 2012;14(3):241-56. doi: 10.1615/intjmedmushr.v14.i3.20. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2012. PMID: 22577975 Review.
Cited by
-
Antrodia cinnamomea Formula Suppresses Prostate Cancer Progression via Immune Modulation and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 17;26(6):2684. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062684. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141325 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Neuroinflammatory Modulators: Therapeutic Potential of Fungi-Derived Compounds in Selected Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2025 Jul 28;30(15):3158. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153158. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal Bioactive Compounds as Emerging Therapeutic Options for Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4800. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104800. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alçada-Morais S., Gonçalves N., Moreno-Juan V., Andres B., Ferreira S., Marques J. M., et al. (2021). Adenosine A2A receptors contribute to the radial migration of cortical projection neurons through the regulation of neuronal polarization and axon formation. Cereb. Cortex 31 (12), 5652–5663. 10.1093/cercor/bhab188 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

