Chinese medicine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology: a review
- PMID: 38694920
- PMCID: PMC11061375
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1381712
Chinese medicine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology: a review
Abstract
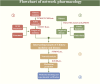
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a clinicopathological syndrome characterized by abnormalities in hepatic fat deposition, the incidence of which has been increasing year by year in recent years. It has become the largest chronic liver disease globally and one of the important causes of cirrhosis and even primary liver cancer formation. The pathogenesis of NAFLD has not yet been fully clarified. Modern medicine lacks targeted clinical treatment protocols for NAFLD, and most drugs lack efficacy and have high side effects. In contrast, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has significant advantages in the treatment and prevention of NAFLD, which have been widely recognized by scholars around the world. In recent years, through the establishment of a "medicine-disease-target-pathway" network relationship, network pharmacology can explore the molecular basis of the role of medicines in disease prevention and treatment from various perspectives, predicting the pharmacological mechanism of the corresponding medicines. This approach is compatible with the holistic view and treatment based on pattern differentiation of TCM and has been widely used in TCM research. In this paper, by searching relevant databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase, we reviewed and analyzed the relevant signaling pathways and specific mechanisms of action of single Chinese medicine, Chinese medicine combinations, and Chinese patent medicine for the treatment of NAFLD in recent years. These related studies fully demonstrated the therapeutic characteristics of TCM with multi-components, multi-targets, and multi-pathways, which provided strong support for the exact efficacy of TCM exerted in the clinic. In conclusion, we believe that network pharmacology is more in line with the TCM mindset of treating diseases, but with some limitations. In the future, we should eliminate the potential risks of false positives and false negatives, clarify the interconnectivity between components, targets, and diseases, and conduct deeper clinical or experimental studies.
Keywords: network pharmacology; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; research progress; review; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Xue, Li, Zao, Li, Liu, Cao, Wang, Qi, Zhang and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine monomer for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 May 5;898:173976. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173976. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33639194 Review.
-
Integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: future directions and strategies.Chin Med. 2024 Feb 3;19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00894-1. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38310315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of multi-omics and network pharmacology to explain traditional chinese medicine for vascular cognitive impairment: A narrative review.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jan;123:155231. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155231. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38007992 Review.
-
Application of herbs and active ingredients ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 20;13:1000727. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1000727. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36204095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the action mechanism of the Polygonum perfoliatum L. on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, based on network pharmacology and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 3):117330. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117330. Epub 2023 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37863399
Cited by
-
The efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine sequential therapy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Feb;41(2):512-518. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.2.11352. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39926655 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics based exploration of the anti-NAFLD mechanism of Wang's empirical formula via TLR4/NF-κB/COX2 pathway.Mol Med. 2024 Dec 27;30(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-01022-3. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39730994 Free PMC article.
-
A Direct Relationship Between 'Blood Stasis' and Fibrinaloid Microclots in Chronic, Inflammatory, and Vascular Diseases, and Some Traditional Natural Products Approaches to Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 12;18(5):712. doi: 10.3390/ph18050712. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patent research in academic literature. Landscape and trends with a focus on patent analytics.Front Res Metr Anal. 2025 Jan 8;9:1484685. doi: 10.3389/frma.2024.1484685. eCollection 2024. Front Res Metr Anal. 2025. PMID: 39844863 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 May 15;18:1599-1627. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S517874. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40391051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources