The Effect of Obesity on Severity of Asthma: An Observational Prospective Study from Pakistan
- PMID: 38694965
- PMCID: PMC11060623
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_238_23
The Effect of Obesity on Severity of Asthma: An Observational Prospective Study from Pakistan
Abstract
Objective: The current research study aimed to access the relationship between obesity and asthma exacerbations and severity among adult patients at the outpatient section of a federal hospital (PIMS) in Islamabad, Pakistan.
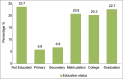
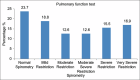
Methods: A cross-sectional research study was carried out on 207 asthma adult patients belonging to different areas and ethnic groups from the country. The study setting was the PIMS hospital, which attracts patients from all over the country due to its facilities and cost-effective treatments. The body mass index (BMI) of asthma patients was calculated using the heights and weights of the study subjects. However, the pulmonary functions were calculated using a computerized spirometer i-e Spirolab III S/N 303681 in line with Winspiro PRO 7.1.version software. It presents the patient's forced vital capacity that expires in the first second of expiration to full (FEV1) in comparison to forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio, that is, Tiffeneau-Pinelli index was also recorded to determine the asthma severity.
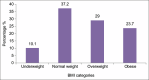
Results: According to recent surveys, the overall prevalence of patients with overweight and obesity was 29.0% and 23.7%, respectively. A Chi-square test was used, and a statistically significant relationship was observed between BMI and asthma severity (P < 0.001). The adult obese female patients presented poor pulmonary functions. The average FEV1/FVC ratio presented significant variance among four different categories of BMI with P < 0.05. This difference was due to the normal BMI category as the Tiffeneau-Pinelli index, that is, FEV1/FVC in the normal BMI group was significantly lower as compared to that in underweight and obese patients.
Conclusion: The study subjects presented raised asthma severity in accordance with the raised BMI. Obese patients presented comparatively raised asthma exacerbations. Moreover, a statistically significant association of gender difference was observed between obesity and asthma severity. It was concluded that adult asthmatic women with obesity presented raised asthma severity as compared to adult asthmatic males.
Keywords: Asthma; body mass index (BMI); forced expiratory volume (FEV1); forced vital capacity (FVC); obesity.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:557–82. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal MS, Al-Saikhan FI, Ahmed NJ, Iqbal MZ. How do out-of-pocket expenditures affect healthcare: A qualitative insight of acute exacerbation among asthma patients. J Pharm Res Int. 2020;32:67–73.
-
- Lalani NS. A study of knowledge assessment and competence in asthma and inhaler technique of nurses employed at university teaching hospital. Health. 2012:316–8.
-
- Shahid S, Ahmed F, Shahnaz G, Saqlain M, Ans M, Sana A, et al. The impact of theoretical and practical guidance regarding metered dose inhaler technique on asthma patients. J Young Pharm. 2022;14:327.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources