Study Design of a Brazilian Observational Study of Edoxaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation (EdoBRA)
- PMID: 38695465
- PMCID: PMC12092049
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20230392
Study Design of a Brazilian Observational Study of Edoxaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation (EdoBRA)
Abstract
Background: Clinical trials showed the safety of Edoxaban, a non-vitamin K-dependent oral anticoagulant (NOAC), and its efficacy to prevent stroke and systemic embolism in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) patients and also to prevent and treat venous thromboembolism. However, additional research is needed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of Edoxaban in a real-world scenario in the Brazilian population.
Objective: In order to understand the risks and benefits of Edoxaban use in routine clinical settings, the EdoBRA study is being conducted to gain insight into the safety and effectiveness of Edoxaban use in non-preselected patients with NVAF in Brazil.
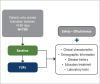
Methods: The EdoBRA study is a multicenter, prospective, observational study conducted in 36 sites in Brazil. NVAF patients ≥ 18 years treated with commercially available Edoxaban who initiated treatment for at least 14 days and no longer than 90 days prior to enrollment, and who are not simultaneously participating in any interventional study are eligible for this study. Seven hundred patients are planned to be enrolled and one-year of follow up, with data collections expected at baseline and 3, 6, and 12 months after the study enrollment. The primary safety objective is ISTH Clinically Relevant Bleeding, and the secondary effectiveness objective focuses on relevant cardiovascular outcomes related to NVAF.
Conclusion: EdoBRA observational study will generate relevant additional information about NOAC Edoxaban on various aspects of patient management in routine care, such as its safety and effectiveness profile in patients with NVAF in Brazil.
Fundamento: Os ensaios clínicos demonstraram a segurança da Edoxabana, um anticoagulante oral não dependente de vitamina K (NOAC), e a sua eficácia na prevenção de acidente vascular cerebral e embolia sistémica em pacientes com fibrilação atrial não valvar (FANV) e também na prevenção e tratamento de tromboembolismo venoso. No entanto, pesquisas adicionais são necessárias para avaliar a segurança e a eficácia da Edoxabana em um cenário real na população brasileira.
Objetivo: A fim de compreender os riscos e benefícios do uso da Edoxabana em cenários clínicos de rotina, o estudo EdoBRA está sendo conduzido para obter informações sobre a segurança e eficácia do uso da Edoxabana em pacientes não pré-selecionados com FANV no Brasil.
Métodos: O estudo EdoBRA é um estudo multicêntrico, prospectivo e observacional, realizado em 36 centros no Brasil. São elegíveis para este estudo pacientes com FANV, ≥ 18 anos de idade, tratados com Edoxabana disponível comercialmente, que iniciaram o tratamento por pelo menos 14 dias e não mais do que 90 dias antes da data de inclusão no estudo, e que não estão participando de nenhum outro estudo de intervenção. Ao todo, 700 pacientes devem ser inscritos e acompanhados por um ano, com coletas de dados programadas para o período basal e 3, 6 e 12 meses após a inscrição no estudo. O objetivo primário de segurança é o sangramento clinicamente relevante (de acordo com critérios da Sociedade Internacional de Trombose e Hemostasia - ISTH), e o objetivo secundário de eficácia são desfechos cardiovasculares relevantes relacionados à FANV.
Conclusão: O estudo observacional EdoBRA gerará informações adicionais relevantes sobre a Edoxabana enquanto NOAC em diversos aspectos do manejo de pacientes no atendimento clínico de rotina, como perfil de segurança e efetividade em pacientes com FANV no Brasil.
Conflict of interest statement
Dalton Bertolim Précoma - Recebeu honorários por palestras científicas patrocinadas pela Daiichi Sankyo e por participação em Conselho Consultivo Científico. Rafael Paletta da Silva – Funcionário da Daiichi Sankyo Brasil. Allyson Nakamoto – Funcionário da Daiichi Sankyo Brasil. Viviane Mariz Omar – Funcionária da Daiichi Sankyo Brasil durante o desenvolvimento do protocolo. Danilo Guidini Lopes - Funcionário da Daiichi Sankyo Brasil durante o desenvolvimento do protocolo. José Francisco Kerr Saraiva - Recebeu honorários por palestras científicas patrocinadas pela Daiichi Sankyo e por participação em Conselho Consultivo Científico.
Figures





References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the Special Contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J . 2021;42(5):373–498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mostaza JM, Suarez C, Cepeda JM, Manzano L, Sánchez D, PERFILAR study investigators Demographic, Clinical, and Functional Determinants of Antithrombotic Treatment in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord . 2021;21(1):384–384. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02019-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magalhães LP, Figueiredo MJO, Cintra FD, Saad EB, Kuniyishi RR, Teixeira RA, et al. II Diretrizes Brasileiras de Fibrilação Atrial. Arq Bras Cardiol . 2016;106(4):1–22. doi: 10.5935/abc.20160055. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

