99mTc-labeled FAPI compounds for cancer and inflammation: from radiochemistry to the first clinical applications
- PMID: 38695960
- PMCID: PMC11065808
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-024-00264-0
99mTc-labeled FAPI compounds for cancer and inflammation: from radiochemistry to the first clinical applications
Abstract
Background: In recent years, fibroblast activating protein (FAP), a biomarker overexpressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts, has emerged as one of the most promising biomarkers in oncology. Similarly, FAP overexpression has been detected in various fibroblast-mediated inflammatory conditions such as liver cirrhosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Along this trajectory, FAP-targeted positron emission tomography (PET), utilizing FAP inhibitors (FAPi) labeled with positron emitters, has gained traction as a powerful imaging approach in both cancer and inflammation. However, PET represents a high-cost technology, and its widespread adoption is still limited compared to the availability of gamma cameras. To address this issue, several efforts have been made to explore the potential of [99mTc]Tc-FAPi tracers as molecular probes for imaging with gamma cameras and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
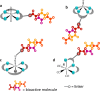
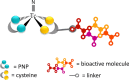
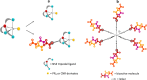
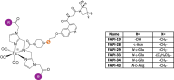
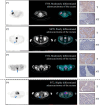
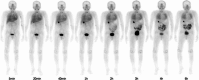
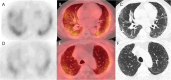
Main body: Several approaches have been investigated for labeling FAPi-based compounds with 99mTc. Specifically, the mono-oxo, tricarbonyl, isonitrile, and HYNIC strategies have been applied to produce [99mTc]Tc-FAPi tracers, which have been tested in vitro and in animal models. Overall, these labeling approaches have demonstrated high efficiency and strong binding. The resulting [99mTc]Tc-FAPi tracers have shown high specificity for FAP-positive cells and xenografts in both in vitro and animal model studies, respectively. However, the majority of [99mTc]Tc-FAPi tracers have exhibited variable levels of lipophilicity, leading to preferential excretion through the hepatobiliary route and undesirable binding to lipoproteins. Consequently, efforts have been made to synthesize more hydrophilic FAPi-based compounds to improve pharmacokinetic properties and achieve a more favorable biodistribution, particularly in the abdominal region. SPECT imaging with [99mTc]Tc-FAPi has yielded promising results in patients with gastrointestinal tumors, demonstrating comparable or superior diagnostic performance compared to other imaging modalities. Similarly, encouraging outcomes have been observed in subjects with gliomas, lung cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. Beyond oncological applications, [99mTc]Tc-FAPi-based imaging has been successfully employed in myocardial and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Conclusions: This overview focuses on the various radiochemical strategies for obtaining [99mTc]Tc-FAPi tracers, highlighting the main challenges encountered and possible solutions when applying each distinct approach. Additionally, it covers the preclinical and initial clinical applications of [99mTc]Tc-FAPi in cancer and inflammation.
Keywords: Fibroblast activation protein; Inflammation; Molecular imaging; Oncology; PET; SPECT.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alberto R, Schibli R, Schubiger AP, Abram U, Pietzsch HJ, Johannsen B. First application of fac-[(99m)Tc(OH2)3(CO)3]+ in bioorganometallic chemistry: design, structure, and in vitro affinity of a 5-HT(1A) receptor ligand labeled with (99m)Tc. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:6076–6077. doi: 10.1021/JA990765A/SUPPL_FILE/JA990765A_S.PDF. - DOI
-
- Bergmann C, Distler JHW, Treutlein C, Tascilar K, Müller AT, Atzinger A, et al. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET-CT for molecular assessment of fibroblast activation and risk evaluation in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: a single-centre, pilot study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3:e185–e194. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30421-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
