A perspective on tumor radiation resistance following high-LET radiation treatment
- PMID: 38696003
- PMCID: PMC11065934
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05757-8
A perspective on tumor radiation resistance following high-LET radiation treatment
Abstract
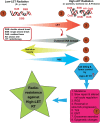
High-linear energy transfer (LET) radiation is a promising alternative to conventional low-LET radiation for therapeutic gain against cancer owing to its ability to induce complex and clustered DNA lesions. However, the development of radiation resistance poses a significant barrier. The potential molecular mechanisms that could confer resistance development are translesion synthesis (TLS), replication gap suppression (RGS) mechanisms, autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) activation, release of exosomes, and epigenetic changes. This article will discuss various types of complex clustered DNA damage, their repair mechanisms, mutagenic potential, and the development of radiation resistance strategies. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of careful consideration and patient selection when employing high-LET radiotherapy in clinical settings.
Keywords: Clustered DNA lesions; Linear energy transfer (LET); Photon therapy; Relative biological effectiveness (RBE); Translesion synthesis (TLS).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to the content of the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

