Identifying lncRNAs and mRNAs related to survival of NSCLC based on bioinformatic analysis and machine learning
- PMID: 38696317
- PMCID: PMC11131976
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205783
Identifying lncRNAs and mRNAs related to survival of NSCLC based on bioinformatic analysis and machine learning
Abstract
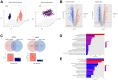
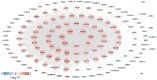
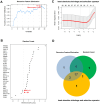
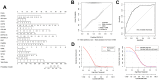
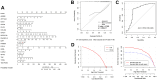
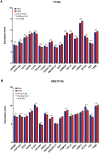
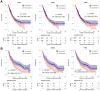
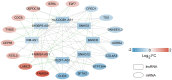
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common histopathological type, and it is purposeful for screening potential prognostic biomarkers for NSCLC. This study aims to identify the lncRNAs and mRNAs related to survival of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The expression profile data of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma were downloaded in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset. A total of eight survival related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and 262 survival related mRNAs were filtered. By gene set enrichment analysis, 17 significantly correlated Gene Ontology signal pathways and 14 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes signal pathways were screened. Based on the clinical survival and prognosis information of the samples, we screened eight lncRNAs and 193 mRNAs by single factor Cox regression analysis. Further single and multifactor Cox regression analysis were performed, 30 independent prognostication-related mRNAs were obtained. The PPI network was further constructed. We then performed the machine learning algorithms (Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, Recursive feature elimination, and Random forest) to screen the optimized DEGs combination, and a total of 17 overlapping mRNAs were obtained. Based on the 17 characteristic mRNAs obtained, we firstly built a Nomogram prediction model, and the ROC values of training set and testing set were 0.835 and 0.767, respectively. By overlapping the 17 characteristic mRNAs and PPI network hub genes, three genes were obtained: CDC6, CEP55, TYMS, which were considered as key factors associated with survival of NSCLC. The in vitro experiments were performed to examine the effect of CDC6, CEP55, and TYMS on NSCLC cells. Finally, the lncRNAs-mRNAs networks were constructed.
Keywords: CDC6; CEP55; NSCLC; machine learning; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Basumallik N, Agarwal M. Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2023. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

