Quality of life and its associated factors in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis from a Peruvian city: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38696413
- PMCID: PMC11065205
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300280
Quality of life and its associated factors in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis from a Peruvian city: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: To assess quality of life and explore its associated factors in a group of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) undergoing hemodialysis in Peru.
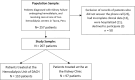
Methodology: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of patients with CKD treated at two medical centers in Tacna, Peru; between July and September 2023. We conducted a survey via telephone interviews with eligible patients using the Short Form 36 (SF 36) to assess their quality of life.
Results: Of 257 patients with CKD undergoing hemodialysis, we successfully interviewed 207 (59.9% males, median age: 62 years, median time on hemodialysis: 3.5 years). In the context of the SF-36 assessment, the dimensions with the lowest scores were physical role (mean: 13.9), emotional role (32.2), and physical function (32.4). Regarding the SF-36 summary scores, the average scores were 42.2 in the mental health domain and 32.0 in the physical health domain. In the adjusted model, the physical health domain score was higher in males (β = 2.7) and those with economic self-sufficiency (β = 3.0) and lower in older adults (β = -2.5). The score in the mental health domain was higher in those with a higher level of education (β = 4.1), in those with economic self-sufficiency (β = 3.8), and in those receiving care at one of the centers included (β: 4.2).
Conclusion: Quality of life was affected, particularly in the realms of physical and emotional well-being. Furthermore, both the physical and mental health domains tend to show lower scores among women, older individuals, those lacking economic self-sufficiency, individuals with lower educational levels, and those with comorbidities.
Copyright: © 2024 Machaca-Choque et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Burden of Kidney Disease, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Employment Among Patients Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis and In-Center Hemodialysis: Findings From the DOPPS Program.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Oct;78(4):489-500.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.02.327. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33872688
-
Factors associated with quality of life among chronic kidney disease patients in Nepal: a cross-sectional study.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Jun 29;18(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01458-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32600360 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond quality of life: a cross sectional study on the mental health of patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing dialysis and their caregivers.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Apr 17;15(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0646-4. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 28412933 Free PMC article.
-
Frailty and quality of life: a cross-sectional study of Brazilian patients with pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Feb 28;12:27. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-27. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 24580960 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of quality of life between patients underwent peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Jun 18;18(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01449-2. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32552800 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Willingness and influencing factors of adults receiving Hemodialysis to use mobile healthcare apps: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04228-7. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40597850 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Impact of Potential Confounders on Health-Related Quality of Life and Physical Activity in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Treated with Dialysis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 17;13(14):1729. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13141729. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724754 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical