Sex differences among subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator recipients: a propensity-matched, multicentre, international analysis from the i-SUSI project
- PMID: 38696701
- PMCID: PMC11100525
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euae115
Sex differences among subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator recipients: a propensity-matched, multicentre, international analysis from the i-SUSI project
Abstract
Aims: Women have been historically underrepresented in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) trials. No data on sex differences regarding subcutaneous ICDs (S-ICD) carriers have been described. Aim of our study was to investigate sex-related differences among unselected S-ICD recipients.
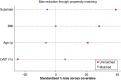
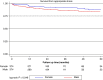
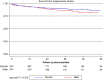
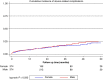
Methods and results: Consecutive patients enrolled in the multicentre, international i-SUSI registry were analysed. Comparisons between sexes were performed using a 1:1 propensity matching adjusted analysis for age, body mass index (BMI), left ventricular function, and substrate. The primary outcome was the rate of appropriate shocks during follow-up. Inappropriate shocks and other device-related complications were deemed secondary outcomes. A total of 1698 patients were extracted from the i-SUSI registry; 399 (23.5%) were females. After propensity matching, two cohorts of 374 patients presenting similar baseline characteristics were analysed. Despite similar periprocedural characteristics and a matched BMI, women resulted at lower risk of conversion failure as per PRAETORIAN score (73.4% vs. 81.3%, P = 0.049). Over a median follow-up time of 26.5 [12.7-42.5] months, appropriate shocks were more common in the male cohort (rate/year 3.4% vs. 1.7%; log-rank P = 0.049), while no significant differences in device-related complications (rate/year: 6.3% vs. 5.8%; log-rank P = 0.595) and inappropriate shocks (rate/year: 4.3% vs. 3.1%; log-rank P = 0.375) were observed. After controlling for confounders, sex remained significantly associated with the primary outcome (aHR 1.648; CI 0.999-2.655, P = 0.048), while not resulting predictor of inappropriate shocks and device-related complications.
Conclusion: In a propensity-matched cohort of S-ICD recipients, women are less likely to experience appropriate ICD therapy, while not showing higher risk of device-related complications.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT0473876.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00473876.
Keywords: Appropriate shocks; Gender differences; S-ICD; Sex differences; Sudden cardiac death.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Schiavone M, Gasperetti A, Laredo M, Breitenstein A, Vogler J, Palmisano P et al. Inappropriate shock rates and long-term complications due to subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in patients with and without heart failure: results from a multicenter, international registry. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2023;16:58–61. - PubMed
-
- van der Heijden AC, Thijssen J, Borleffs CJ, van Rees JB, Höke U, van der Velde ET et al. Gender-specific differences in clinical outcome of primary prevention implantable cardioverter defibrillator recipients. Heart 2013;99:1244–9. - PubMed

