Multimodal analysis of cfDNA methylomes for early detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions
- PMID: 38697989
- PMCID: PMC11065998
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47886-1
Multimodal analysis of cfDNA methylomes for early detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions
Abstract
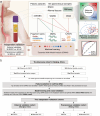
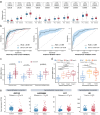
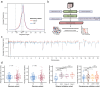
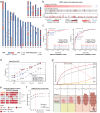
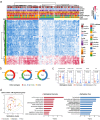
Detecting early-stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and precancerous lesions is critical for improving survival. Here, we conduct whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) on 460 cfDNA samples from patients with non-metastatic ESCC or precancerous lesions and matched healthy controls. We develop an expanded multimodal analysis (EMMA) framework to simultaneously identify cfDNA methylation, copy number variants (CNVs), and fragmentation markers in cfDNA WGBS data. cfDNA methylation markers are the earliest and most sensitive, detectable in 70% of ESCCs and 50% of precancerous lesions, and associated with molecular subtypes and tumor microenvironments. CNVs and fragmentation features show high specificity but are linked to late-stage disease. EMMA significantly improves detection rates, increasing AUCs from 0.90 to 0.99, and detects 87% of ESCCs and 62% of precancerous lesions with >95% specificity in validation cohorts. Our findings demonstrate the potential of multimodal analysis of cfDNA methylome for early detection and monitoring of molecular characteristics in ESCC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Development and validation of predictive models for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its precancerous lesions using terminal motif analysis in circulating cell-free DNA].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 23;46(6):549-565. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20231207-00353. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38880735 Chinese.
-
Genome-Scale Multimodal Analysis of Cell-Free DNA Whole-Methylome Sequencing for Noninvasive Esophageal Cancer Detection.JCO Precis Oncol. 2024 Jun;8:e2400111. doi: 10.1200/PO.24.00111. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38976830
-
Early Diagnostic Markers for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Copy Number Alteration Gene Identification and cfDNA Detection.Lab Invest. 2024 Oct;104(10):102127. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2024.102127. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Lab Invest. 2024. PMID: 39182610
-
Tissue protein biomarker candidates to predict progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Dec;1434(1):59-69. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13863. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 29882970 Review.
-
Circulating cell-free DNA-based methylation pattern in plasma for early diagnosis of esophagus cancer.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 31;12:e16802. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16802. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38313016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cell-free-DNA-based diagnostics.Genome Res. 2025 Jan 22;35(1):1-19. doi: 10.1101/gr.278413.123. Genome Res. 2025. PMID: 39843210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and fragmentomic landscapes of cell-free DNA for early cancer detection.Nat Rev Cancer. 2025 May;25(5):341-358. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00795-x. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Nat Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40038442 Review.
-
Hypermethylation of miR-129-2-3p inhibits esophageal cancer proliferation and migration by down-regulating PPP6C expression.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Feb 25;17(2):1459-1469. doi: 10.62347/WJGT6717. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40092081 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of esophageal cancer: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Biomark Res. 2025 Jan 6;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00718-2. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 39762900 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy response monitoring in blood plasma from esophageal adenocarcinoma patients using cell-free DNA methylation profiling.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82325-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82030089/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82188102/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82272938/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 20220484059/Beijing Nova Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

