Isolation of nucleic acids using liquid-liquid phase separation of pH-sensitive elastin-like polypeptides
- PMID: 38698072
- PMCID: PMC11065875
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60648-9
Isolation of nucleic acids using liquid-liquid phase separation of pH-sensitive elastin-like polypeptides
Abstract
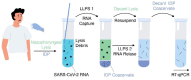
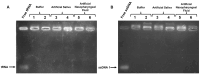
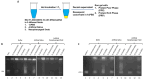
Extraction of nucleic acids (NAs) is critical for many methods in molecular biology and bioanalytical chemistry. NA extraction has been extensively studied and optimized for a wide range of applications and its importance to society has significantly increased. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of early and efficient NA testing, for which NA extraction is a critical analytical step prior to the detection by methods like polymerase chain reaction. This study explores simple, new approaches to extraction using engineered smart nanomaterials, namely NA-binding, intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs), that undergo triggered liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). Two types of NA-binding IDPs are studied, both based on genetically engineered elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs), model IDPs that exhibit a lower critical solution temperature in water and can be designed to exhibit LLPS at desired temperatures in a variety of biological solutions. We show that ELP fusion proteins with natural NA-binding domains can be used to extract DNA and RNA from physiologically relevant solutions. We further show that LLPS of pH responsive ELPs that incorporate histidine in their sequences can be used for both binding, extraction and release of NAs from biological solutions, and can be used to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in samples from COVID-positive patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
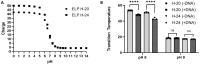
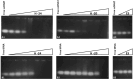
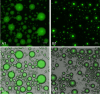
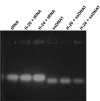
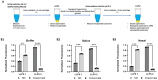
Similar articles
-
Elastin-like polypeptides as models of intrinsically disordered proteins.FEBS Lett. 2015 Sep 14;589(19 Pt A):2477-86. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.08.029. Epub 2015 Aug 29. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26325592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protease-Driven Phase Separation of Elastin-Like Polypeptides.Biomacromolecules. 2024 Aug 12;25(8):4898-4904. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00346. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Biomacromolecules. 2024. PMID: 38980747
-
Effects of Doxorubicin on the Liquid-Liquid Phase Change Properties of Elastin-Like Polypeptides.Biophys J. 2018 Oct 16;115(8):1431-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 30292393 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative model of the phase behavior of recombinant pH-responsive elastin-like polypeptides.Biomacromolecules. 2010 Nov 8;11(11):2873-9. doi: 10.1021/bm100571j. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Biomacromolecules. 2010. PMID: 20925333 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembling systems comprising intrinsically disordered protein polymers like elastin-like recombinamers.J Pept Sci. 2022 Jan;28(1):e3362. doi: 10.1002/psc.3362. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Pept Sci. 2022. PMID: 34545666 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging regulatory mechanisms and functions of biomolecular condensates: implications for therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 6;10(1):4. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02070-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39757214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dhaliwal A. DNA extraction and purification. Mater. Methods. 2013;3:191. doi: 10.13070/mm.en.3.191. - DOI
-
- 2D PAGE: Sample Preparation and Fractionation. vol. 424 (Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

