Elevated serum homocysteine levels associated with poor recurrence-free and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38698172
- PMCID: PMC11066114
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60855-4
Elevated serum homocysteine levels associated with poor recurrence-free and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer
Abstract
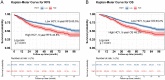
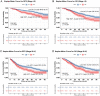
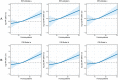
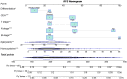
This study aimed to evaluate the significance of homocysteine (HCY) levels in predicting recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. This retrospective study involved 1272 CRC patients. The risk of mortality increased with increasing HCY levels in CRC patients. The optimal HCY cutoff value in CRC patients was 15.2 μmol/L. The RFS (45.8% vs. 60.5%, p < 0.001) and OS (48.2% vs. 63.2%, p < 0.001) of patients with high HCY levels were significantly lower than those of patients with low HCY levels. Patients with high HCY levels were older, male, had large tumours, high carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels, and long hospital stays, and incurred high hospitalisation costs. Multivariate analysis showed that when HCY levels exceeded 15.2 μmol/L, the risk of adverse RFS and OS increased by 55.7% and 61.4%, respectively. Subgroup analysis showed that HCY levels could supplement CEA levels and pathological staging. We constructed HCY-based prognostic nomograms, which demonstrated feasible discrimination and calibration values better than the traditional tumour, node, metastasis staging system for predicting RFS and OS. Elevated serum HCY levels were strongly associated with poor RFS and OS in CRC patients. HCY-based prognostic models are effective tools for a comprehensive evaluation of prognosis.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Homocysteine; Malnutrition; Nomogram; Prognostic.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Grading carcinoembryonic antigen levels can enhance the effectiveness of prognostic stratification in patients with colorectal cancer: a single-centre retrospective study.BMJ Open. 2024 Oct 29;14(10):e084219. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-084219. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39477273 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum carcinoembryonic antigen level after curative surgery is a prognostic biomarker of stage II-III colorectal cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021 Nov;47(11):2880-2887. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.05.041. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34103245
-
Preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen19-9 and carbohydrate antigen 125 as prognostic factors for recurrence-free survival in colorectal cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(5):1251-6. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 21875276
-
Elevated CA19-9 within the normal range suggests poorer prognosis in stage II CRC: A retrospective analysis of a large sample in a single center.J Cancer Res Ther. 2024 Dec 1;20(7):2013-2020. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_338_24. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Cancer Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39792411
-
Homocysteine: A novel prognostic biomarker in liver transplantation for alpha-fetoprotein- negative hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2020;29(2):197-206. doi: 10.3233/CBM-201545. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 32623388
Cited by
-
Colorectal Cancer: Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapy.MedComm (2020). 2025 Mar 6;6(3):e70127. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70127. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40060193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances on the Role of B Vitamins in Cancer Prevention and Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 25;26(5):1967. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051967. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a chemiluminescent immunoassay based on magnetic solid phase for quantification of homocysteine in human serum.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 9;24(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00903-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39385151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Micu BV, Vesa ŞC, Pop TR, Micu CM. Evaluation of prognostic factors for 5 year-survival after surgery for colorectal cancer. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2020;91:41–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

