Association between serum sodium trajectory and mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38698368
- PMCID: PMC11067220
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03586-y
Association between serum sodium trajectory and mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Dysnatremia is strongly associated with poor prognosis in acute kidney injury (AKI); however, the impact of sodium trajectories on the prognosis of patients with AKI has not yet been well elucidated. This study aimed to assess the association between sodium trajectories in patients with AKI and mortality at 30-day and 1-year follow-up.
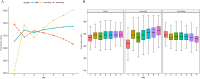
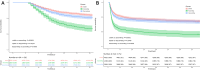
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used data from Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV database, and patients diagnosed with AKI within 48 h after admission were enrolled. Group-based trajectory models (GBTM) were applied to map the developmental course of the serum sodium fluctuations. Kaplan-Meier survival curve was used to compare differences in mortality in AKI patients with distinct serum sodium trajectories. Hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated to determine the association between trajectories and prognosis using Cox proportional hazard models.
Results: A total of 9,314 AKI patients were enrolled. Three distinct sodium trajectories were identified including: (i) stable group (ST, in which the serum sodium levels remained relatively stable, n = 4,935; 53.0%), (ii) descending group (DS, in which the serum sodium levels declined, n = 2,994; 32.15%) and (iii) ascending group (AS, in which the serum sodium levels were elevated, n = 1,383; 14.85%). There was no significant difference in age and gender distribution among the groups. The 30-day mortality rates were 7.9% in ST, 9.5% in DS and 16.6% in AS (p < 0.001). The results of 1-year mortality rates were similar (p < 0.001). In adjusted analysis, patients in the DS (HR = 1.22, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-1.43, p = 0.015) and AS (HR = 1.68, 95% CI, 1.42-2.01, p = 0.013) groups had higher risks of 30-day mortality compared to those in the ST group.
Conclusion: In patients with AKI, the serum sodium trajectories were independently associated with 30-day and 1-year mortality. Association between serum sodium level trajectories and prognosis in patients with AKI deserve further study.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cohort study; MIMIC database; Mortality; Serum sodium trajectory.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Admission serum sodium and potassium levels predict survival among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Aug 8;20(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1505-9. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31395027 Free PMC article.
-
Association between hemoglobin glycation index and poor prognosis in patients with AKI: a retrospective cohort analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2499232. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2499232. Epub 2025 May 13. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40356360 Free PMC article.
-
Heart failure subphenotypes based on mean arterial pressure trajectory identify patients at increased risk of acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2452205. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2452205. Epub 2025 Jan 19. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 39829038 Free PMC article.
-
The association between lactate dehydrogenase to serum albumin ratio and the 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in intensive care: a retrospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2212080. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2212080. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37194715 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cell distribution width predicts long-term mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective database study.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 12;10(1):4563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61516-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32165684 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between trajectory of triglyceride-glucose index and all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with atrial fibrillation: a retrospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02838-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40640797 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of serum calcium levels on the occurrence of sepsis and prognosis in hospitalized patients with concomitant psoriasis: a retrospective study based on the MIMIC-IV database.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 22;16:1621231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1621231. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40766324 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of lactate trajectory models for predicting acute kidney injury and mortality in patients with hyperlactatemia: insights across three independent cohorts.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2474205. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2474205. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40074720 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

