Dimeric Bis-Benzimidazole-Pyrroles DB2Py(n) - AT-Site-Specific Ligands: Synthesis, Physicochemical Analysis, and Biological Activity
- PMID: 38698958
- PMCID: PMC11062108
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.27327
Dimeric Bis-Benzimidazole-Pyrroles DB2Py(n) - AT-Site-Specific Ligands: Synthesis, Physicochemical Analysis, and Biological Activity
Abstract
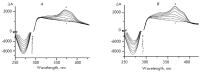
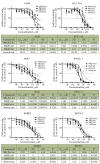
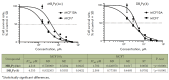
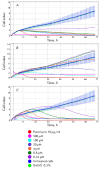
Its broad spectrum of biological activity makes benzimidazole a fundamental pharmacophore in pharmaceutics. The paper describes newly synthesized AT-specific fluorescent bis-benzimidazole molecules DB2Py(n) that contain a pyrrolcarboxamide fragment of the antibiotic drug netropsin. Physico-chemical methods using absorption, fluorescence, and circular dichroism spectra have shown the ability of bis-benzimidazole- pyrroles to form complexes with DNA. The new DB2Py(n) series have turned out to be more toxic to human tumor lines and less vulnerable to non-tumor cell lines. Bis-benzimidazole-pyrroles penetrated the cell nucleus, affected the cell-cycle synthesis (S) phase, and inhibited eukaryotic topoisomerase I in a cellfree model at low concentrations. A real-time tumor cell proliferation test confirmed the molecule's enhanced toxic properties upon dimerization. Preliminary cytotoxicity data for the bis-benzimidazole-pyrroles tested in a cell model with a MDR phenotype showed that monomeric compounds can overcome MDR, while dimerization weakens this ability to its intermediate values as compared to doxorubicin. In this respect, the newly synthesized cytotoxic structures seem promising for further, in-depth study of their properties and action mechanism in relation to human tumor cells, as well as for designing new AT-specific ligands.
Keywords: DNA narrow groove binding ligand; DNA-binding; bis-benzimidazole-pyrrole; cell cycle; cytotoxicity; multidrug resistance; topoisomerase I.
Copyright ® 2024 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 1,2,5-trisubstituted benzimidazole derivatives as cytotoxic agents endowed with ABCB1 inhibitory action to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer cells.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2710-2724. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2127700. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36168121 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-selective targeting of long stretches of the DNA minor groove by a novel dimeric bis-benzimidazole.Biochemistry. 2003 May 27;42(20):5984-92. doi: 10.1021/bi026926w. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12755600
-
Netropsin and bis-netropsin analogs as inhibitors of the catalytic activity of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II and topoisomerase cleavable complexes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 27;1090(1):52-60. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90036-l. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991. PMID: 1653020
-
New Pyrrole Derivatives as Promising Biological Agents: Design, Synthesis, Characterization, In Silico, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 9;23(16):8854. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168854. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012121 Free PMC article.
-
The development of bis(hydroxymethyl)pyrrole analogs as bifunctional DNA cross-linking agents and their chemotherapeutic potential.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Nov;69:609-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.09.016. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24095754 Review.
References
-
- Venugopal S., Kaur B., Verma A., Wadhwa P., Magan M., Hudda S., Kakoty V., Chem. Biol. Drug Design. 2023;102:357–376. - PubMed
-
- Wu K., Peng X., Chen M., Li Y., Tang G., Peng J., Peng Y., Cao X., Chem. Biol. Drug Design. 2022;99(5):736–757. - PubMed
-
- Tyagi Y.K., Jali G., Singh R.. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022;22(19):3280–3290. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov A.A., Salyanov V.I., Strel’tsov S.A., Cherepanova N.A., Gromova E.S., Zhuze A.L., Rus. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2011;37(4):530–541. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
