The Effect of Calcium Ions on the Electrophysiological Properties of Single ANO6 Channels
- PMID: 38698960
- PMCID: PMC11062105
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.27338
The Effect of Calcium Ions on the Electrophysiological Properties of Single ANO6 Channels
Abstract
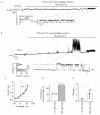
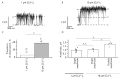
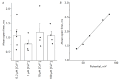
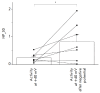
Proteins belonging to the anoctamin (ANO) family form calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCCs). The most unusual member of this family, ANO6 (TMEM16F), simultaneously exhibits the functions of calcium-dependent scramblase and the ion channel. ANO6 affects the plasma membrane dynamics and phosphatidylserine transport; it is also involved in programmed cell death. The properties of ANO6 channels remain the subject of debate. In this study, we investigated the effect of variations in the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of calcium ions on the electrophysiological properties of endogenous ANO6 channels by recording single ANO6 channels. It has been demonstrated that (1) a high calcium concentration in an extracellular solution increases the activity of endogenous ANO6 channels, (2) the permeability of endogenous ANO6 channels for chloride ions is independent of the extracellular concentration of calcium ions, (3) that an increase in the intracellular calcium concentration leads to the activation of endogenous ANO6 channels with double amplitude, and (4) that the kinetics of the channel depend on the plasma membrane potential rather than the intracellular concentration of calcium ions. Our findings give grounds for proposing new mechanisms for the regulation of the ANO6 channel activity by calcium ions both at the inner and outer sides of the membrane.
Keywords: ANO6; TMEM16F; calcium-activated chloride channels; patch-clamp technique; recording currents through single channels.
Copyright ® 2024 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ion channel and lipid scramblase activity associated with expression of TMEM16F/ANO6 isoforms.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;593(17):3829-48. doi: 10.1113/JP270691. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26108457 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TMEM16A/ANO1 and TMEM16F/ANO6 ion currents and phospholipid scrambling by Ca2+ and plasma membrane lipid.J Physiol. 2018 Jan 15;596(2):217-229. doi: 10.1113/JP275175. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29134661 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium chelation independent effects of BAPTA on endogenous ANO6 channels in HEK293T cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Jan 22;693:149378. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.149378. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38100999
-
Mechanisms of cellular synchronization in the vascular wall. Mechanisms of vasomotion.Dan Med Bull. 2010 Oct;57(10):B4191. Dan Med Bull. 2010. PMID: 21040688 Review.
-
Molecular functions of anoctamin 6 (TMEM16F): a chloride channel, cation channel, or phospholipid scramblase?Pflugers Arch. 2014 Mar;466(3):407-14. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1305-1. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 23748496 Review.
References
-
- Ehlen H.W.A., Chinenkova M., Moser M., Munter H.M., Krause Y., Gross S., Brachvogel B., Wuelling M., Kornak U., Vortkamp A., J. Bone Mineral Res. 2013;28(2):246–259. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
