Integrated assessment of irrigation and agriculture management challenges in Nepal: An interdisciplinary perspective
- PMID: 38698972
- PMCID: PMC11064071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29407
Integrated assessment of irrigation and agriculture management challenges in Nepal: An interdisciplinary perspective
Abstract
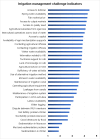
Agriculture plays a critical role in ensuring food and nutrition security, livelihood, and rural employment in Nepal. Despite substantial investments and institutional reforms, irrigation projects have faced consistently low performance. While existing studies have shed light on technical aspects of irrigation performance, they often focus on specific themes rather than holistic evaluations of sustainability. This research systematically assesses barriers and challenges to effective irrigation water management in Nepal by assessing and ranking the challenges faced by three irrigation systems in western Nepal: Mahakali, Rani Jamara Kulariya, and Babai. To investigate these challenges, we collected data from 449 households, which provided insights into 33 indicators representing key barriers to effective irrigation and agricultural management. The identified challenges were categorized into four broad thematic areas: physical and structural, agricultural and water, socioeconomic and market, and gender and governance. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted to compare these challenges among the three irrigation schemes, different thematic areas, and various locations within each scheme (namely, the head, mid, and tail sections of the system). The findings revealed that timely access and availability of fertilizers, spring water availability and fair market prices of agricultural products are the most significant challenges. The Babai irrigation system faced the most substantial challenges among the three systems, particularly in the mid section. These findings emphasize the interconnectedness of these challenges, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to planning, implementation, and management. Integrated strategies are essential to address socioeconomic, market, and endogenous farming issues, ensuring reliable irrigation water availability for sustainable agricultural production.
Keywords: Holistic assessment; Likert scale; Western Nepal; agriculture water; gender and governance; socioeconomic and market.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Local irrigation management institutions mediate changes driven by external policy and market pressures in Nepal and Thailand.Environ Manage. 2010 Sep;46(3):411-23. doi: 10.1007/s00267-010-9544-9. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Environ Manage. 2010. PMID: 20721664
-
Implementing conjunctive management of water resources for irrigation development: A framework applied to the Southern Plain of Western Nepal.Agric Water Manag. 2023 Jun 1;283:108287. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108287. Agric Water Manag. 2023. PMID: 37265577 Free PMC article.
-
Fair and sustainable irrigation water management in the Babai basin, Nepal.Water Sci Technol. 2009;59(8):1505-13. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.150. Water Sci Technol. 2009. PMID: 19403963
-
Deficit irrigation and sustainable water-resource strategies in agriculture for China's food security.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(8):2253-69. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv034. Epub 2015 Apr 3. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25873664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrition and food security in Nepal: a narrative review of policies.Nutr Rev. 2023 Nov 10;81(12):1612-1625. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad025. Nutr Rev. 2023. PMID: 36944110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative performance assessment of pilot irrigation schemes in Uganda.Heliyon. 2024 May 21;10(10):e31600. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31600. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38826721 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Cultivation Area, Demographic Trends, and Trade Dynamics for Food Security in Nepal (2011-2021).Plant Environ Interact. 2024 Dec 6;5(6):e70020. doi: 10.1002/pei3.70020. eCollection 2024 Dec. Plant Environ Interact. 2024. PMID: 39649068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu B., Tian F., Zhang M., Piao S., Zeng H., Zhu W., Liu J., Elnashar A., Lu Y. Quantifying global agricultural water appropriation with data derived from earth observations. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;358 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131891. - DOI
-
- WB World Bank's online database. 2020. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ER.H2O.FWAG.ZS?locations=NP
-
- DWRI . Department of Water Resources and Irrigation Ministry of Energy, Water Resources, and Irrigation, Government of Nepal; Kathmandu, Nepal: 2019. Irrigation Master Plan. DRAFT.
-
- Pradhan P. Revitalizing irrigation systems for food security: Vision and approaches in Nepal irrigation systems. Hydro Nepal. Journal of Water, Energy and Environment. 2012:44–49.
-
- MoEWRI . Government of Nepal; 2023. National Irrigation Policy 2023. Ministry of Water Energy, Water Resources and Irrigation (MoEWRI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

