Unlocking the Potential: A Systematic Literature Review on the Impact of Donor Human Milk on Infant Health Outcomes
- PMID: 38699095
- PMCID: PMC11064102
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57440
Unlocking the Potential: A Systematic Literature Review on the Impact of Donor Human Milk on Infant Health Outcomes
Abstract
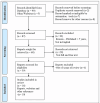
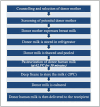
Human mother milk is considered the most healthy and best source of nutrition for both premature and full-term infants, as it possesses many health benefits and is associated with its consumption. Some of the mothers are not able to produce an adequate quantity of milk to meet the required needs of the infants, particularly in cases involving premature births or facing challenges in breastfeeding. Especially for the most vulnerable premature infants, donor human milk (DHM) provides a helpful bridge for effective breastfeeding. Even with the advancement in baby formulas, no other dietary source can match the bioactive matrix of benefits found in human breast milk. This literature review discusses the risks associated with prematurity and explores the use of DHM in the care of premature infants. It helps prevent substantial preterm complications, especially necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and late-onset sepsis, which are more commonly seen in infants who are given formulated milk made from cow's milk. It gives insights into the benefits of DHM, such as immunological and nutritional benefits, which is a basic infant's need. When medical distress prevents mothers from producing enough breast milk for their infants, pasteurized human donor breast milk should be made accessible as an alternative feeding option to ensure infants remain healthy and nourished. A systematic literature search was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar databases and other sources. A total of 104 articles were searched, of which 35 were included after identification, filters were applied, eligibility was checked, and references out of scope were excluded. Human milk banking should be incorporated into programs encouraging breastfeeding, highlighting lactation in mothers and only using DHM when required.
Keywords: human milk bank; immunity; lactation management; low birth weight; preterm.
Copyright © 2024, Kashyap et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Call for authors - systematic reviews on donor human milk banking processes . [ Dec; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/articles-detail/call-for-authors-systemati... https://www.who.int/news-room/articles-detail/call-for-authors-systemati...
-
- National guidelines on lactation management centres in public health facilities. https://nhm.gov.in/images/pdf/programmes/IYCF/National_Guidelines_Lactat... [ Dec; 2023 ]. 2017. National guidelines on lactation management centres in public health facilities.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
