Indian Clinician's Perspective on the Approach to the Management of Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38699103
- PMCID: PMC11063652
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57435
Indian Clinician's Perspective on the Approach to the Management of Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
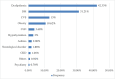
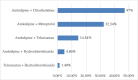
Introduction Hypertension (HTN) is considered one of the most frequent life-threatening noncommunicable illnesses. Because HTN has a significant public health impact on cardiovascular health status and healthcare systems in India, it is critical to study Indian clinicians' approaches to HTN management. Methodology This was a cross-sectional, multicentric, non-interventional, and single-visit study that aimed to gather data from across India and examine sociodemographic characteristics and clinician treatment choices in the management of HTN in Indian individuals. As a result, building an information platform about HTN is critical to preventing and controlling this growing burden. Results A total of 5298 patients were recruited in the study from 1061 study centers across India. Among the study patients, 66.67% were females with a mean age of 53.95 ± 14.4, and 66.28% of hypertensive patients presented comorbidities. Among the known risk factors for HTN, 2227 (44.5%) were smokers, while 2587 (51.7%) had sedentary lifestyles. A family history of HTN in either one or both parents was seen in 1076 (21.50%) patients. In management, 40.40% of patients were on anti-hypertensive monotherapy. Amlodipine (41.8%) in monotherapy and amlodipine + metoprolol (32.34%) in combination therapy were the most commonly prescribed antihypertensive. Conclusion Management of HTN can be improved by imparting patient education and awareness about the need for medication compliance, lifestyle modifications, and regular follow-up clinic visits.
Keywords: antihypertensive; hypertension; management; perspective; sedentary lifestyle.
Copyright © 2024, Ram et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials