Identification of shared molecular mechanisms and diagnostic biomarkers between heart failure and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 38699746
- PMCID: PMC11063427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30086
Identification of shared molecular mechanisms and diagnostic biomarkers between heart failure and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are global public health concerns. The relationship between HF and IPF is widely acknowledged. However, the interaction mechanisms between these two diseases remain unclear, and early diagnosis is particularly difficult. Through the integration of bioinformatics and machine learning, our work aims to investigate common gene features, putative molecular causes, and prospective diagnostic indicators of IPF and HF.
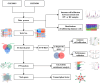
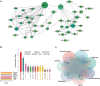
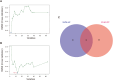
Methods: The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database provided the RNA-seq datasets for HF and IPF. Utilizing a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), possible genes linked to HF and IPF were found. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO) were then employed to analyze the genes that were shared by HF and IPF. Using the cytoHubba and iRegulon algorithms, a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network was built based on seven basic diagnostic indicators. Additionally, hub genes were identified using machine learning approaches. External datasets were used to validate the findings. Lastly, the association between the number of immune cells in tissues and the discovered genes was estimated using the CIBERSORT method.
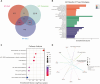
Results: In total, 63 shared genes were identified between HF- and IPF-related modules using WGCNA. Extracellular matrix (ECM)/structure organization, ECM-receptor interactions, focal, and protein digestion and absorption, were shown to be the most enrichment categories in GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of common genes. Furthermore, a total of seven fundamental genes, including COL1A1, COL3A1, THBS2, CCND1, ASPN, FAP, and S100A12, were recognized as pivotal genes implicated in the shared pathophysiological pathways of HF and IPF, and TCF12 may be the most important regulatory transcription factor. Two characteristic molecules, CCND1 and NAP1L3, were selected as potential diagnostic markers for HF and IPF, respectively, using a support vector machine-recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) model. Furthermore, the development of diseases and diagnostic markers may be associated with immune cells at varying degrees.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that ECM/structure organisation, ECM-receptor interaction, focal adhesion, and protein digestion and absorption, are common pathogeneses of IPF and HF. Additionally, CCND1 and NAP1L3 were identified as potential diagnostic biomarkers for both HF and IPF. The results of our study contribute to the comprehension of the co-pathogenesis of HF and IPF at the genetic level and offer potential biological indicators for the early detection of both conditions.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Diagnostic biomarkers; Heart failure; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; SVM-RFE; WGCNA.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of Hub Genes and Pathways Associated With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Aug 12;8:711239. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.711239. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34476240 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers and immune microenvironment associated with heart failure through bioinformatics and machine learning.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 8;12:1580880. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1580880. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40406620 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the shared diagnostic genes and mechanisms between periodontitis and primary Sjögren's syndrome by integrated comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and machine learning.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;141:112899. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112899. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39142001
-
Identification of oxidative stress-related diagnostic markers and immune infiltration features for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by bibliometrics and bioinformatics.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;11:1356825. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1356825. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT4 and COL1A2 are potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for heart failure comorbided with depression.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Jun 15;184:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35367598 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Causal Relationship Between Plasma Proteins and Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Analysis Based on Mendelian Randomization.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 14;14(2):200. doi: 10.3390/biology14020200. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001968 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerators of chronic hepatitis B fibrosis cirrhosis CCND1 gene expression and promoter hypomethylation.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 27;15(1):10630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93778-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40148411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanai E., Frantz S. Pathophysiology of heart failure. Compr. Physiol. 2015;6(1):187–214. - PubMed
-
- McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., Chioncel O., et al. Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2023;2023
-
- Roger V.L. Epidemiology of heart failure: a Contemporary perspective. Circ. Res. 2021;128(10):1421–1434. - PubMed
-
- Savarese G., Becher P.M., Lund L.H., Seferovic P., Rosano G.M.C., Coats A.J.S. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023;118(17):3272–3287. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

