Jerks are useful: extracting pulse rate from wrist-placed accelerometry jerk during sleep in children
- PMID: 38700932
- PMCID: PMC11807889
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/zsae099
Jerks are useful: extracting pulse rate from wrist-placed accelerometry jerk during sleep in children
Abstract
Study objectives: Evaluate wrist-placed accelerometry predicted heartrate compared to electrocardiogram (ECG) heartrate in children during sleep.
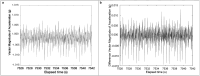
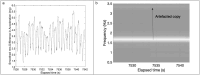
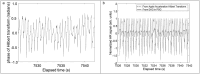
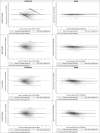
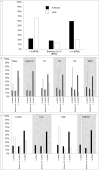
Methods: Children (n = 82, 61% male, 43.9% black) wore a wrist-placed Apple Watch Series 7 (AWS7) and ActiGraph GT9X during a polysomnogram. Three-Axis accelerometry data was extracted from AWS7 and the GT9X. Accelerometry heartrate estimates were derived from jerk (the rate of acceleration change), computed using the peak magnitude frequency in short time Fourier Transforms of Hilbert transformed jerk computed from acceleration magnitude. Heartrates from ECG traces were estimated from R-R intervals using R-pulse detection. Lin's concordance correlation coefficient (CCC), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percent error (MAPE) assessed agreement with ECG estimated heart rate. Secondary analyses explored agreement by polysomnography sleep stage and a signal quality metric.
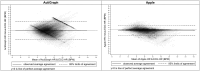
Results: The developed scripts are available on Github. For the GT9X, CCC was poor at -0.11 and MAE and MAPE were high at 16.8 (SD = 14.2) beats/minute and 20.4% (SD = 18.5%). For AWS7, CCC was moderate at 0.61 while MAE and MAPE were lower at 6.4 (SD = 9.9) beats/minute and 7.3% (SD = 10.3%). Accelerometry estimated heartrate for AWS7 was more closely related to ECG heartrate during N2, N3 and REM sleep than lights on, wake, and N1 and when signal quality was high. These patterns were not evident for the GT9X.
Conclusions: Raw accelerometry data extracted from AWS7, but not the GT9X, can be used to estimate heartrate in children while they sleep. Future work is needed to explore the sources (i.e. hardware, software, etc.) of the GT9X's poor performance.
Keywords: actigraphy; ambulatory sleep monitoring; children; heart rate variability; open source; pediatrics – behavior; sleep tracking; validation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Sleep Research Society. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Goldstone A, Baker FC, Zambotti M. de.. Actigraphy in the digital health revolution: still asleep? Sleep. 2018;41(9). doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy120 - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Zambotti M, Goldstein C, Cook J, et al.State of the science and recommendations for using wearable technology in sleep and circadian research. Sleep. 2023;47:zsad325. - PubMed
-
- Van De Water AT, Holmes A, Hurley DA.. Objective measurements of sleep for non-laboratory settings as alternatives to polysomnography–a systematic review. J Sleep Res. 2011;20(1pt2):183–200. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2009.00814.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Zambotti M, Goldstone A, Claudatos S, Colrain IM, Baker FC.. A validation study of Fitbit Charge 2™ compared with polysomnography in adults. Chronobiol Int. 2018;35(4):465–476. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/07420528.2017.1413578 - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Zambotti M, Baker FC, Willoughby AR, et al.Measures of sleep and cardiac functioning during sleep using a multi-sensory commercially-available wristband in adolescents. Physiol Behav. 2016;158:143–149. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.03.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P20 GM130420/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK136205/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL171295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL171295/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- FA9550-23-1-0506/Air Force Office of Scientific Research
- T32GM081740/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM081740/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK129215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM145226/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM130420/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N00014-18-1-2429/Office of Naval Research
- ECCS2246582/National Science Foundation
- R01DK129215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

