Initial clinical experience with the balloon-in-basket pulsed field ablation system: acute results of the VOLT CE mark feasibility study
- PMID: 38701222
- PMCID: PMC11098042
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euae118
Initial clinical experience with the balloon-in-basket pulsed field ablation system: acute results of the VOLT CE mark feasibility study
Abstract
Aims: Pulsed field ablation (PFA) for the treatment of atrial fibrillation (AF) potentially offers improved safety and procedural efficiencies compared with thermal ablation. Opportunities remain to improve effective circumferential lesion delivery, safety, and workflow of first-generation PFA systems. In this study, we aim to evaluate the initial clinical experience with a balloon-in-basket, 3D integrated PFA system with a purpose-built form factor for pulmonary vein (PV) isolation.
Methods and results: The VOLT CE Mark Study is a pre-market, prospective, multi-centre, single-arm study to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the Volt™ PFA system for the treatment of paroxysmal (PAF) or persistent AF (PersAF). Feasibility sub-study subjects underwent phrenic nerve evaluation, endoscopy, chest computed tomography, and cerebral magnetic resonance imaging. Study endpoints were the rate of primary serious adverse event within 7 days and acute procedural effectiveness. A total of 32 subjects (age 61.6 ± 9.6 years, 65.6% male, 84.4% PAF) were enrolled and treated in the feasibility sub-study and completed a 30-day follow-up. Acute effectiveness was achieved in 99.2% (127/128) of treated PVs (96.9% of subjects, 31/32) with 23.8 ± 4.2 PFA applications/subject. Procedure, fluoroscopy, LA dwell, and transpired ablation times were 124.6 ± 28.1, 19.8 ± 8.9, 53.0 ± 21.0, and 48.0 ± 19.9 min, respectively. Systematic assessments of initial safety revealed no phrenic nerve injury, pulmonary vein stenosis, or oesophageal lesions causally related to the PFA system and three subjects with silent cerebral lesions (9.4%). There were no primary serious adverse events.
Conclusion: The initial clinical use of the Volt PFA System demonstrates acute safety and effectiveness in the treatment of symptomatic, drug refractory AF.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Balloon; Basket; Pulsed field ablation; Single shot.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest P.S. reports serving on the medical advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Boston-Scientific, CathRx, and Pacemate. The University of Adelaide has received on behalf of P.S. research funds from Boston-Scientific, Medtronic, Abbott, and Becton Dickenson. S.H. reports teaching and consulting honorariums for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, and Johnson and Johnson. S.H. also serves on the medical advisory boards for Biotronik and Boston Scientific. The Victorian Heart Hospital has also received research funds from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Abbott on behalf of S.H. The University of Adelaide has received advisory and/or consulting fees on behalf of M.E. from Medtronic and Biosense Webster. E.K. reports serving on the medical advisory boards for Medtronic, Boston-Scientific, and Biotronik. A.M. is employed by Abbott. J.M.K. reports research and fellowship support from Medtronic, Biosense Webster, Abbott, and Zoll.
Figures


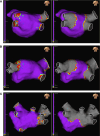

References
-
- Reddy VY, Neuzil P, Koruth JS, Petru J, Funosako M, Cochet H et al. Pulsed field ablation for pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;74:315–26. - PubMed
-
- Turagam MK, Neuzil P, Schmidt B, Reichlin T, Neven K, Metzner A et al. Safety and effectiveness of pulsed field ablation to treat atrial fibrillation: one-year outcomes from the MANIFEST-PF registry. Circulation 2023;148:35–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

