Research hotspots and trends of complementary and alternative therapy for neuropathic pain: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38701253
- PMCID: PMC11062655
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038054
Research hotspots and trends of complementary and alternative therapy for neuropathic pain: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain (NP) is a common type of pain in clinic. Due to the limited effect of drug treatment, many patients with NP are still troubled by this disease. In recent years, complementary and alternative therapy (CAT) has shown good efficacy in the treatment of NP. As the interest in CAT for NP continues to grow, we conducted a bibliometric study of publications on CAT treatment for NP. The aim of this study is to analyze the development overview, research hotspots and future trends in the field of CAT and NP through bibliometric methodology, so as to provide a reference for subsequent researchers.
Methods: Publications on CAT in the treatment of NP from 2002 to 2022 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. Relevant countries, institutions, authors, journals, keywords, and references were analyzed bibliometrically using Microsoft Excel 2021, bibliometric platform, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace.
Results: A total of 898 articles from 46 countries were published in 324 journals, and they were contributed by 4455 authors from 1102 institutions. The most influential country and institution are China (n = 445) and Kyung Hee University (n = 63), respectively. Fang JQ (n = 27) and Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine (n = 63) are the author and journal with the most publications in this field. The clinical efficacy, molecular biological mechanisms and safety of CAT for NP are currently hot directions. Low back pain, postherpetic neuralgia, acupuncture, and herbal are the hot topics in CAT and NP in recent years.
Conclusion: This study reveals the current status and hotspots of CAT for NP. The study also indicates that the effectiveness and effect mechanism of acupuncture or herbs for treating emotional problems caused by low back pain or postherpetic neuralgia may be a trend for future research.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
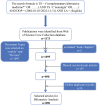
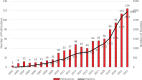
Figures








References
-
- Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G. Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:807–19. - PubMed
-
- Finnerup NB, Kuner R, Jensen TS. Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev. 2021;101:259–301. - PubMed
-
- Silva RL, Lopes AH, Guimarães RM, et al. . CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling in pathological pain: role in peripheral and central sensitization. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;105:109–16. - PubMed
-
- Rice ASC, Smith BH, Blyth FM. Pain and the global burden of disease. Pain. 2016;157:791–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

